Definition- The ratio of RMS value to the average value of alternating quantities -voltage or current is called the form factor. The form factor term is used with alternating voltage and current because they have different RMS and average values. Let us first understand what is the alternating current.
What is Alternating Current?
As its name suggests, alternating means charging its direction. The alternating current periodically changes its direction. On the other hand, the direct current flows in only one direction. The waveform of the alternating current is given below.

What is Form Factor of AC in Electrical?
The form factor represents the physical shape of the AC waveform. The factor changes with a change in the shape of the waveform because its RMS and average value change. Thus, the form factor is very important in electrical engineering to understand AC waveform characteristics.
The form factor is a numerical value that is equal to the ratio between the root mean square (RMS) value and the average value of the waveform.
Form Factor Formula
The following mathematical formula can express it.
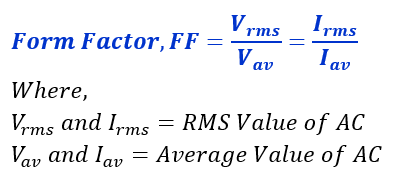
The RMS Value is the effective value of voltage and current, and It is calculated by taking the square root of the average of the squares of all the instantaneous values of the waveform over a complete cycle. In other words, the RMS value is equal to the arithmetic mean value of these instantaneous values.
Form Factor Derivation of AC
The form factor of the perfect sinusoidal voltage or current can be calculated as follows.

Therefore,

You can calculate the form factor by dividing the RMS value of the waveform by its average value. If the RMS value of the AC wave is 25 volts and the average value is 22.52 volts, then the form factor of the AC wave is 25/22.52=1.11. If the value of form factor of a waveform is 1.11, then it is a perfect sinusoidal waveform, and it shows that the RMS value of the waveform is 1.11 times greater than its average value.
Importance of Form Factor
The form factor of AC is important because of the following reasons
- The change in the form factor can be determined by analyzing the wave shape. The FF deviation from 1.11 shows the distorted waveform, and this contains the harmonics. The distorted waveform causes power losses in the transmission network and thus deteriorates the transmission efficiency.
- The losses in the electrical machines increase with distorted waveform.
- The measuring instrument for the perfect sinusoidal waveform read less or more for the waveshape with FF other than 1.11.
- The FF impacts the useful life of electrical equipment.
How to Measure and Calculate Form Factor?
The following methods can be used to measure and calculate FF of AC.
- Cathode Ray Oscilloscope(CRO) displays the waveform on its screen visually. You can visually inspect the waveform for any distortion. The CRO also displays the RMS and average value, and by dividing the RMS by the average value, you can calculate the form factor of AC.
- You can use a True RMS multimeter to measure the RMS and average value. The meter directly outputs the FF of AC.
Form Factor of Various AC Waveforms in Electrical
| S.No. | Type of Wave | Form Factor(FF) |
| 1. | Sinusoidal wave | π/2√2 = 1.11072073 |
| 2. | Rectified sine wave (half-wave ) | π/2 = 1.5707963 |
| 3. | Rectified sine wave (full-wave ) | π/2√2 = 1.11072073 |
| 4. | Square wave | 1/1= 1 |
| 5. | Triangular waveform | 2/√3 = 1.15470054 |
| 6. | Sawtooth waveform | 2/√3 = 1.15470054 |
| 7. | Pulse wave | √D/D=√D |
| 8. | Gaussian noise | 1/√3/ 1/2=2/√3 |
Solved Problem on Form Factor
The maximum or peak value of AC is 600 volts. Calculate the FF of voltage waveform.
The RMS value of AC

The Average value of AC

FF of AC

Conclusion
The form factor of AC is a very important parameter and deviation of FF from its specified value deteriorates the power transmission efficiency, device performance, and useful life of equipment. The insightful knowledge of FF helps in designing and optimizing AC systems and equipment. Engineers and technicians can regularly monitor form factors( FF) to ensure AC power systems’ reliable and efficient operation.
FAQs
Form factor in electrical engineering is the ratio of the RMS (Root Mean Square) value of a waveform to its average value. It helps to understand the shape of AC waveforms like sine, square, or triangular waves.
In an AC circuit, the form factor indicates how the RMS voltage or current compares to the average value, giving insight into waveform efficiency and power delivery.
The form factor helps in calculating the effective voltage or current for power computations, designing electrical equipment, and ensuring proper sizing of conductors and transformers.
Form factor= RMS Value/Avergae Value=Vrms/Vav
The general formula is RMS value divided by the average value. Specific waveforms like half-wave, full-wave, or triangular AC have their own derived formulas based on waveform shape.
Sinusoidal AC: 1.11
Square wave: 1.0
Triangular wave: 1.15
Form factor compares RMS to average value, while peak factor (crest factor) compares peak value to RMS value. Both describe waveform characteristics but highlight different aspects.
No, form factor is a dimensionless ratio.
Related Artciles: