High tension(HT) power cable plays a critical role in power transmission systems. These cables carry high-voltage electricity from power stations to substations, industrial setups, and commercial buildings, ensuring uninterrupted energy flow. Whether you are an engineer, electrician, or student, understanding high tension cables—their types, parts, sizing, and applications—is essential for safe and efficient power distribution.
What is a High Tension (HT) Cable?
The full form of HT cable is High Tension Cable. A high tension HT cable is an electrical cable designed to transmit electricity at high voltages, usually above 11 kV. Unlike low tension (LT) cables, HT cables are designed to handle higher currents and voltages, requiring robust insulation, armoring, and mechanical protection.
These cables are also known as high tension wires and are widely used in:
- Power transmission lines
- Industrial power systems
- Substations and large electrical installations
Key Features of HT Cables:
- High voltage capability (11 kV to 33 kV or more)
- Thick multi-layered insulation
- Strong mechanical protection
- Long-distance transmission suitability
Types of HT Cables
HT cables are broadly divided into three categories depending on their voltage rating:
| Type | Voltage Range | Common Applications |
| Low Voltage (LV) | 1.1 kV – 3.3 kV | Small industrial units, commercial premises |
| Medium Voltage (MV) | 3.3 kV – 36 kV | Substations, medium industries, city distribution |
| Extra High Voltage (EHV) | 66 kV – 220 kV | Power transmission over long distances, large substations |
Each voltage type can further be classified based on core, conductor material, size, insulation, and mechanical strength.
1. Low Voltage (LV) HT Cable
- Voltage Range: 1.1 kV to 3.3 kV
- Core Type: Single core or three core
- Conductor Material: Copper or Aluminum
- Cable Size:
- Single core: 10 sq.mm to 1000 sq.mm
- Three core: 6 sq.mm to 630 sq.mm
- Insulation: PVC or XLPE
- Mechanical Protection: Armoured or Unarmoured
Note: LV HT cables are widely used for local distribution in industries and commercial buildings.
2. Medium Voltage (MV) HT Cable
- Voltage Range: 3.3 kV to 36 kV
- Core Type: Single core or three core
- Conductor Material: Copper or Aluminum
- Cable Size:
- Single core: 25 sq.mm to 1000 sq.mm
- Three core: 25 sq.mm to 400 sq.mm
- Insulation: XLPE
- Mechanical Protection: Armoured or Unarmoured
Use Case: MV HT cables are suitable for substations, city power distribution networks, and medium industries, where reliable power flow is required.
3. Extra High Voltage (EHV) HT Cable
- Voltage Range: 66 kV to 220 kV
- Core Type: Single core (mostly)
- Conductor Material: Copper or Aluminum
- Insulation: XLPE
- Mechanical Protection: Armoured or Unarmoured
- Cable Size Examples:
The table below shows common sizes for copper and aluminum conductors, helping in the selection of appropriate cables for EHV applications:
| Voltage | Copper Conductor | Aluminum Conductor |
| 38/66 kV (72.5 kV) | 240 – 2500 sq.mm | 400 – 2500 sq.mm |
| 64/110 kV (123 kV) | 240 – 2500 sq.mm | 400 – 2500 sq.mm |
| 76/132 kV (145 kV) | 300 – 2500 sq.mm | 400 – 2500 sq.mm |
| 127/220 kV (245 kV) | 400 – 2500 sq.mm | 400 – 2500 sq.mm |
EHV HT cables are designed for long-distance power transmission, connecting major substations or industrial zones.
Parts of a High Tension (HT) Cable
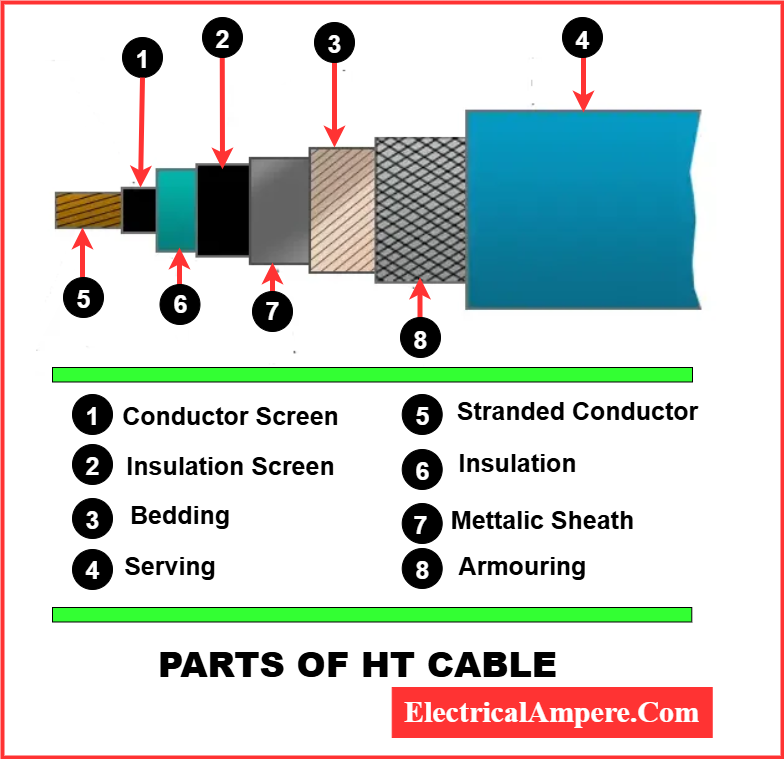
A typical HT cable has multiple layers, each serving a specific purpose. Understanding these parts is crucial for installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
1. Conductor
- The central metallic core, usually made of copper or aluminum.
- Conducts electricity efficiently with minimal losses.
2. Conductor Screen
- Semi-conductive layer around the conductor.
- Smoothens electric field distribution and reduces stress on insulation.
3. Insulation
- Thick layer surrounding the conductor.
- Materials used: XLPE, PVC, rubber
- Protects against electrical leakage and short circuits.
4. Insulation Screen
- Semi-conductive layer over insulation.
- Enhances voltage distribution and protects insulation integrity.
5. Metallic Sheath
- Usually made of aluminum or copper tape.
- Provides mechanical protection and shields against electromagnetic interference (EMI).
6. Armoring
- Optional layer, typically steel wire or tape, for underground cables.
- Protects the cable from mechanical damage, rodents, and external forces.
7. Outer Sheath
- Final protective layer.
- Protects against moisture, chemicals, UV radiation, and mechanical stress.
HT Cable Size and Selection
Choosing the correct HT cable size is essential to ensure safe operation and efficiency. Cable size depends on:
- Load current: Higher current requires larger conductor cross-section.
- Voltage level: HT line voltage ranges from 11 kV to 33 kV.
- Installation type: Underground, overhead, or duct installation affects cable design.
- Material: Copper requires smaller cross-section than aluminum for the same current.
Example of HT Cable Sizes:
- 3-core, 240 sq.mm copper cable for 33 kV industrial feeder line
- 3-core, 95 sq.mm aluminum cable for 11 kV substation connection
Tip: Oversized cables reduce energy loss but increase cost, while undersized cables overheat and reduce service life.
Key Differences Between HT and LT Cables
| Aspect | HT Cable | LT Cable |
| Voltage | Above 11 kV | Up to 1.1 kV |
| Insulation | Thick, multi-layered | Thin |
| Application | Transmission, industrial supply | Domestic, commercial |
| Conductor Material | Copper or Aluminum | Copper or Aluminum |
| Cable Size | Larger (e.g., 240 sq.mm) | Smaller (e.g., 16–95 sq.mm) |
Note: LT cable full form is Low Tension Cable, designed for lower voltage applications.
Applications of HT Cables
HT cables are used across various sectors:
- Power transmission lines from power plants to substations
- Industrial power systems for large machinery
- Renewable energy projects like solar and wind farms
- High-rise buildings and commercial complexes
- Underground city power distribution
Safety Considerations
When working with HT cables, safety is paramount:
- Use insulated tools and personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Avoid direct contact with energized cables.
- Ensure proper earthing and grounding during installation.
- Follow standard electrical codes and regulations.
Conclusion
High tension cables are vital for efficient and safe electricity transmission. Knowing their types, parts, sizing, and applications helps ensure a reliable power network. Proper selection and maintenance of HT cables, high tension wires, and HT line systems minimize energy losses, improve safety, and increase operational efficiency.
Understanding HT cable size, insulation type, and conductor material ensures that power is transmitted effectively over long distances, supporting industrial, commercial, and residential needs.
Related Articles:
- Types of Cable Trays and Sizes
- Difference Between a Cable Ladder and Cable Tray
- KW to Cable Selection Chart and Amp Chart
- Underground Cable Construction
- FRP Ladder Type Cable Tray
- HT Switchgears: Types, Components & How They Work
- What Are LT and HT Panels? Types, Uses, and Key Differences
- What is the Difference Between HT and LT Motor?
- What is LT and HT Line? Difference Between LT and HT?
- EHT Full Form in Electrical: Meaning, Voltage Range & Applications
- What is SWA Cable? Meaning, Full Form, and Applications