DC motors play a vital role in powering modern technology — from electric vehicles and industrial machinery to robotics and automation systems. These motors are known for their precise speed control, fast response, and excellent starting torque. However, like every technology, DC motors also have a few limitations that make them less ideal in certain conditions. In this article, let’s explore the 9 major advantages and disadvantages of DC motor in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
Advantages of DC Motor
DC motors offer several key benefits that make them perfect for applications demanding accuracy, flexibility, and high torque.
1. Excellent Speed Control
DC motors provide smooth and wide-range speed variation. You can easily adjust their speed by changing the armature voltage or field current, which makes them ideal for robotics, electric traction, and automation systems.
2. High Starting Torque
These motors generate very high torque at startup, allowing them to handle heavy loads such as cranes, elevators, and electric trains effortlessly. In many cases, the starting torque can be as high as 500% of the rated torque.
3. Quick and Smooth Response
DC motors respond instantly to changes in control signals. This makes them perfect for systems requiring precise motion control and fast acceleration or deceleration, such as in servo systems.
4. Simple Speed Regulation
Speed regulation in a DC motor is straightforward. With simple control circuits, you can increase or decrease speed without using complex drives or controllers.
5. Easy Maintenance and Operation
DC motors have a simple mechanical design. Replacing brushes or checking commutators is easy, making them user-friendly and serviceable.
6. Reliable and Stable Performance
They provide steady speed and torque even under varying loads, ensuring consistent operation in industrial processes and automation lines.
7. Compact and Versatile Design
The compact build of DC motors makes them suitable for space-limited and portable systems like electric tools and mobile robots.
8. Better Load Handling
They can withstand sudden load changes without major speed fluctuations, making them ideal for variable-load environments.
9. High Efficiency at Low Speed
Unlike AC motors, DC motors maintain good efficiency at low speeds, which is beneficial in conveyors, rolling mills, and other low-speed applications.
Disadvantages of DC Motor
Despite their excellent performance, DC motors have some drawbacks that affect their usability in certain applications.
1. Regular Maintenance Needed
The brushes and commutators wear out due to continuous friction and must be replaced regularly, increasing maintenance efforts and downtime.
2. Higher Initial Cost
DC motors generally cost more to manufacture and install than AC motors, mainly because of their complex construction and control systems.
3. Brush and Commutator Problems
Continuous contact between brushes and the commutator can cause sparks, noise, and heat generation, reducing motor life.
4. Not Suitable for Hazardous Areas
Because of the sparking issue, DC motors are unsafe for use in explosive or flammable environments, such as chemical plants or oil refineries.
5. Limited Speed Range
Operating a DC motor beyond its rated speed can lead to excessive wear, vibration, and mechanical damage.
6. Heavier and Bulkier Design
For the same power output, DC motors are often larger and heavier than equivalent AC motors, which limits their use in compact applications.
7. Requires DC Power Supply
DC motors require a direct current source, which may not always be available, especially in areas relying on AC mains supply.
8. Overheating Under Heavy Load
Prolonged high-load operation can cause overheating and insulation failure, leading to performance issues or breakdown.
9. Lower Efficiency at High Loads
At higher load conditions, energy losses due to brush friction and armature heating can reduce overall efficiency.
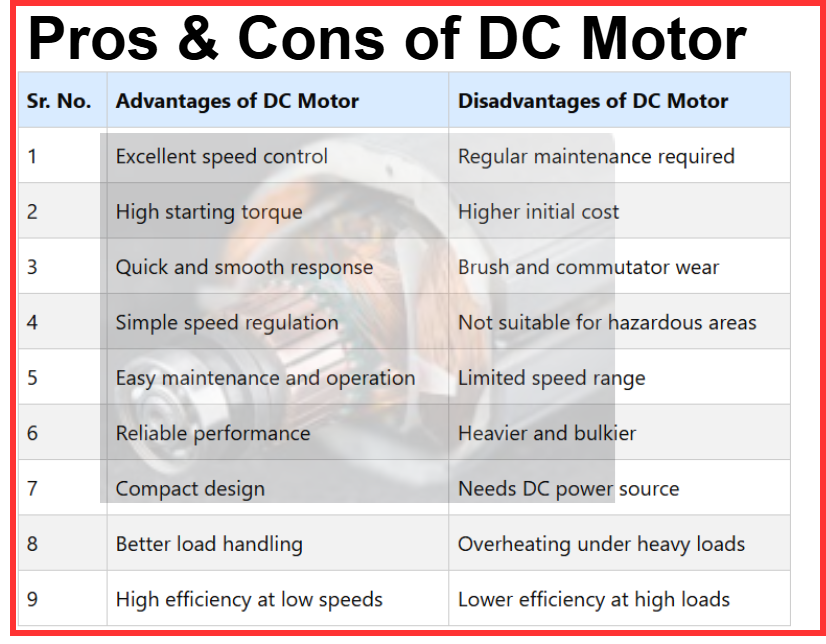
Summary Table: Advantages and Disadvantages of DC Motor
| Sr. No. | Advantages of DC Motor | Disadvantages of DC Motor |
| 1 | Excellent speed control | Regular maintenance required |
| 2 | High starting torque | Higher initial cost |
| 3 | Quick and smooth response | Brush and commutator wear |
| 4 | Simple speed regulation | Not suitable for hazardous areas |
| 5 | Easy maintenance and operation | Limited speed range |
| 6 | Reliable performance | Heavier and bulkier |
| 7 | Compact design | Needs DC power source |
| 8 | Better load handling | Overheating under heavy loads |
| 9 | High efficiency at low speeds | Lower efficiency at high loads |
Applications of DC Motor
DC motors are used in numerous applications that require precision, control, and variable speed, including:
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid cars
- Robotics and automation systems
- Cranes, hoists, and elevators
- Conveyor belts and rolling mills
- Machine tools and textile machinery
- Portable drills and electric tools
- Railway traction and trolleys
Conclusion
DC motors remain one of the most versatile and efficient types of electric motors. Their excellent speed control, high torque, and fast response make them a top choice for electric mobility and automation.
However, the maintenance needs, higher cost, and brush-related issues restrict their use in some industries.
By understanding both the advantages and disadvantages of DC motor, engineers can make informed decisions to select the right motor for specific industrial, automotive, or robotic applications — balancing performance, reliability, and cost effectively.
Related Articles:
- Speed Control Methods of DC Motor – Armature, Flux & Voltage Control Explained
- Speed Regulation of DC Motor: Definition, Formula, Example
- Speed Equation of DC Motor: Explained with Formula and Example
- Regenerative Braking in DC Motor
- DC Series Motor Explained : Working, Construction, Diagram, and Applications
- Speed Control of DC Series Motor: Methods, Diagrams Explained
- Speed Control of DC Shunt Motor: Methods, Diagrams & Formulas