A suspension type insulator is a key component in overhead power transmission, designed to handle high voltages with safety and reliability. Its modular structure allows engineers to adjust the number of units as per voltage requirements, making it suitable for long-span lines and extra-high voltage (EHV) applications.
What is a Suspension Type Insulator?
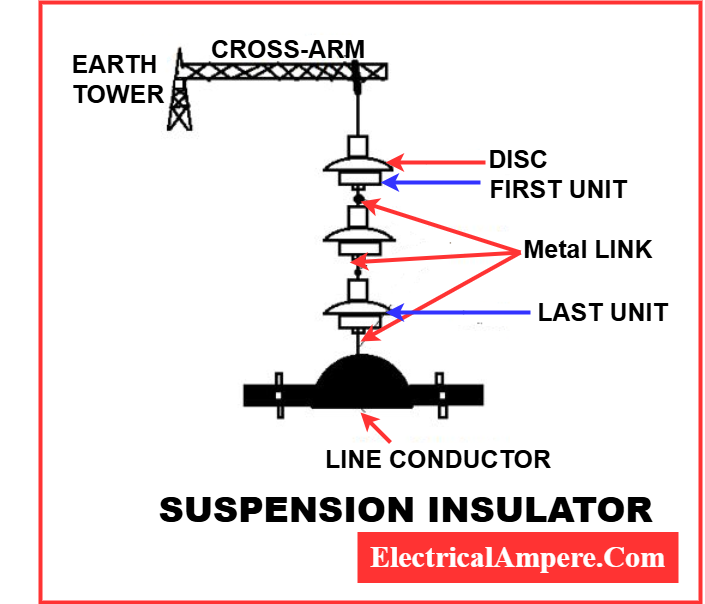
The main function of a suspension insulator is to separate the line conductors and support them electrically. It comprises several porcelain insulator units connected by metal links to form a flexible string. The conductor is usually connected to the bottom of the string.
Suspension Insulator Diagram
The suspension type insulator diagram below illustrates how the porcelain units are arranged in a string.

Working Principle of Suspension Type Insulator
A suspension type insulator consists of several porcelain or glass discs connected in series to form a flexible string. The main principle is voltage distribution across each disc in the string, ensuring that no single unit is overstressed.
Step-by-Step Working:
- Each disc in the string acts as an individual insulator unit.
- The applied line voltage is divided equally among all discs in the string.
- If one disc fails, the remaining discs continue to support the conductor mechanically, preventing complete line failure.
- The string is flexible, allowing it to swing or absorb mechanical stresses from wind or conductor tension.
- Metallic links and fittings transfer mechanical loads while porcelain/glass provides electrical insulation.
Types of Suspension Insulators
There are two main types of suspension insulators
- Cap and Pin Type
- Hewlett or Interlink Type
Below is a detailed explanation of the cap-and-pin, and Hewlett-type insulator.
1. Cap-and-pin type Suspension Insulator
A porcelain cap-and-pin unit is connected by either a ball and socket or clevis-pin to a galvanized cast iron or forged steel cap and a galvanized forged steel pin.
2. Interlink Type Insulator
The unit uses porcelain with two curved channels intersecting at right angles. U-shaped covered steel links pass through these channels to connect the unit. This type of insulator is known as the Hewlett insulator.
The interlink-type insulators are mechanically stronger than the cap-and-pin type units. The metallic link continues to support the line even if the porcelain between the links breaks; thus, the supply is not interrupted.
The Hewlett-type insulator has one major disadvantage: the porcelain between the links is highly electrically stressed, causing its puncture stress to be less than that of other types.
String Efficiency of Suspension Type Insulators
Definition: String efficiency refers to the effectiveness of a suspension insulator string in distributing the applied voltage equally across all units. It is defined as the ratio of the voltage across the entire string to the sum of voltages across individual units.
Key Points:
- Less than 100%: Due to uneven voltage distribution caused by capacitance between each unit and the tower, string efficiency is always slightly below 100%.
- Improving Efficiency:
- Use grading rings (corona rings) to reduce voltage stress on end units.
- Increase the number of units in the string for higher voltage lines.
- Typical Efficiency:
- Depends on the number of discs, tower height, and line voltage. Efficiency usually ranges from 80% to 95%.
Importance: Higher string efficiency ensures better insulation performance, reduces the risk of flashover, and prolongs insulator life.
Advantages of Suspension Type Insulator
These high-voltage overhead line insulators offer the following advantages,
- Depending on the voltage, the appropriate number of discs are connected in series with the string, with each unit operating at about 11kV.These insulators are typically used for voltages above 33 kV and can be employed up to 765 kV or more in extra high voltage (EHV) transmission lines.
- If one unit is damaged, it can be replaced instead of the entire string.
- The transmission line provides great flexibility as the string can swing freely in any direction.
- The suspension insulators are placed above the conductors, and thus, they provide partial lightning protection.
Disadvantages of Suspension Type Insulator
- Higher Initial Cost: Suspension insulators cost more than pin or post types because they use multiple units and fittings.
- Frequent Maintenance: Pollution and weather can affect each unit in the string, so they require regular cleaning and inspection.
- Heavier Setup: Their weight demands stronger and more expensive supporting structures.
- Time-Consuming Installation: Assembling and aligning several discs takes more time during installation.
- Requires More Clearance: Higher voltage needs longer strings, which increases the required vertical clearance.
Applications of Suspension Type Insulator
Suspension insulators are widely used in high-voltage transmission and distribution systems due to their modular construction and mechanical strength. Typical applications include:
- Overhead power lines operating at voltages above 33 kV, often going up to 765 kV or more in extra high voltage (EHV) and ultra-high voltage (UHV) systems.
- Long-span line crossings, such as over rivers or valleys, where mechanical flexibility is essential.
- Substations and switchyards, where space constraints and high voltages require reliable support and insulation.
- Railway electrification systems for power distribution to locomotives.
- Polluted or coastal environments, where longer insulator strings reduce leakage current and flashover risk.
Environmental Considerations
Suspension type insulators are exposed to various environmental conditions, which can affect their performance. Proper selection and design help ensure reliability even in challenging environments.
Key Points:
- Coastal Areas: Salt deposits can form on insulator surfaces, increasing leakage current. Longer strings and periodic cleaning are recommended.
- Industrial/Heavily Polluted Areas: Dust, smoke, and chemical pollution can reduce insulation efficiency. Anti-pollution coatings or shed designs help prevent flashover.
- Rain and Humidity: Wet conditions can create a conductive path along the insulator surface, so appropriate creepage distance is necessary.
- UV and Weather Resistance: Porcelain, glass, and composite materials are chosen for their ability to withstand sun, wind, and temperature variations.
By considering environmental factors during design and maintenance, suspension insulators maintain high reliability and long service life even in harsh conditions.
Maintenance Tips for Suspension Type Insulators
Regular maintenance ensures suspension type insulators perform reliably and have a long service life. Key maintenance practices include:
- Cleaning:
- In polluted or coastal areas, insulator surfaces should be cleaned periodically to remove dust, salt, and chemical deposits.
- Cleaning frequency depends on the severity of pollution.
- Inspection:
- Regularly check for cracks, chips, or other mechanical damage in the porcelain or glass discs.
- Inspect metallic fittings for corrosion or loosening.
- Replacement:
- If a single disc is damaged, it can be replaced without dismantling the entire string.
- Ensure proper alignment and torque of metallic links and fittings during reassembly.
- Record-Keeping:
- Maintain a log of inspections, cleaning, and replacements to monitor performance trends and anticipate potential failures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, suspension insulators play a vital role in overhead power transmission. They offer robust support and reliable insulation for conductors. The Cap and Pin and Composite Suspension Insulators have advantages like high mechanical strength and resistance to environmental factors.
Reference: Insulators used in Transmission Line-Electricalvolt.com
Related Articles: