The star connection 3 phase system—also known as the three-phase star configuration—is a widely adopted method for structuring electrical networks. It plays a key role in enabling efficient power generation, safe transmission, and reliable distribution. This type of connection, also called the Y-connection, is popular because it is easy to use, flexible, and can supply both three-phase and single-phase loads.
In this article, we’ll explore the star connection in a three-phase system in detail. You’ll learn how it works, what the diagram looks like, where it’s commonly used, and why it’s preferred in various electrical setups. We’ll also compare it with delta connections and look into its use in transformer configurations.
What is a Star Connection in a 3-Phase System?
In a three-phase star connection, engineers connect one end of each phase winding to a common point called the neutral. The other ends link to the three line conductors. This arrangement resembles a “Y” shape, which explains its name.
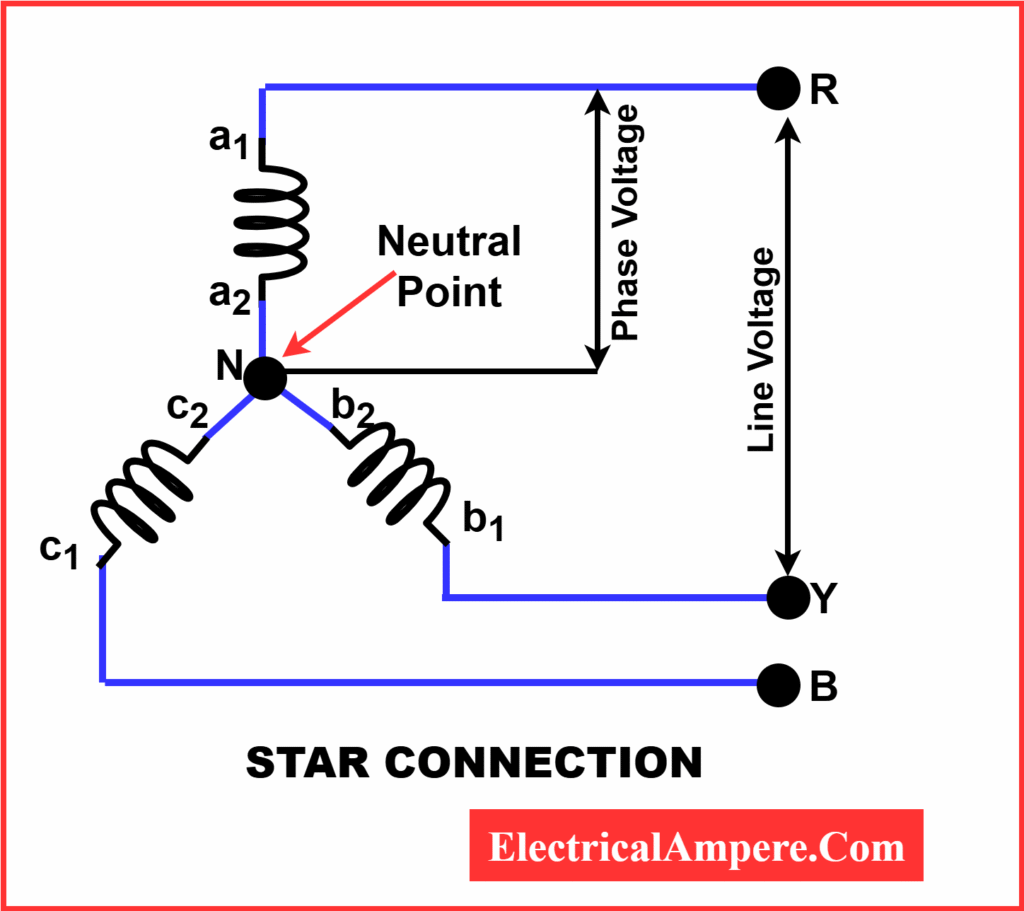
By design, the star connection offers two types of output voltages:
- Line-to-neutral voltage (phase voltage)
- Line-to-line voltage (line voltage)
This flexibility makes it ideal for systems that power both single-phase and three-phase loads.
Star Connection Diagram with Phase and Line Voltage
Let’s look at a typical star connection diagram. It consists of three windings (marked R, Y, and B) that connect at one central point—the neutral. The other ends extend to the line conductors.
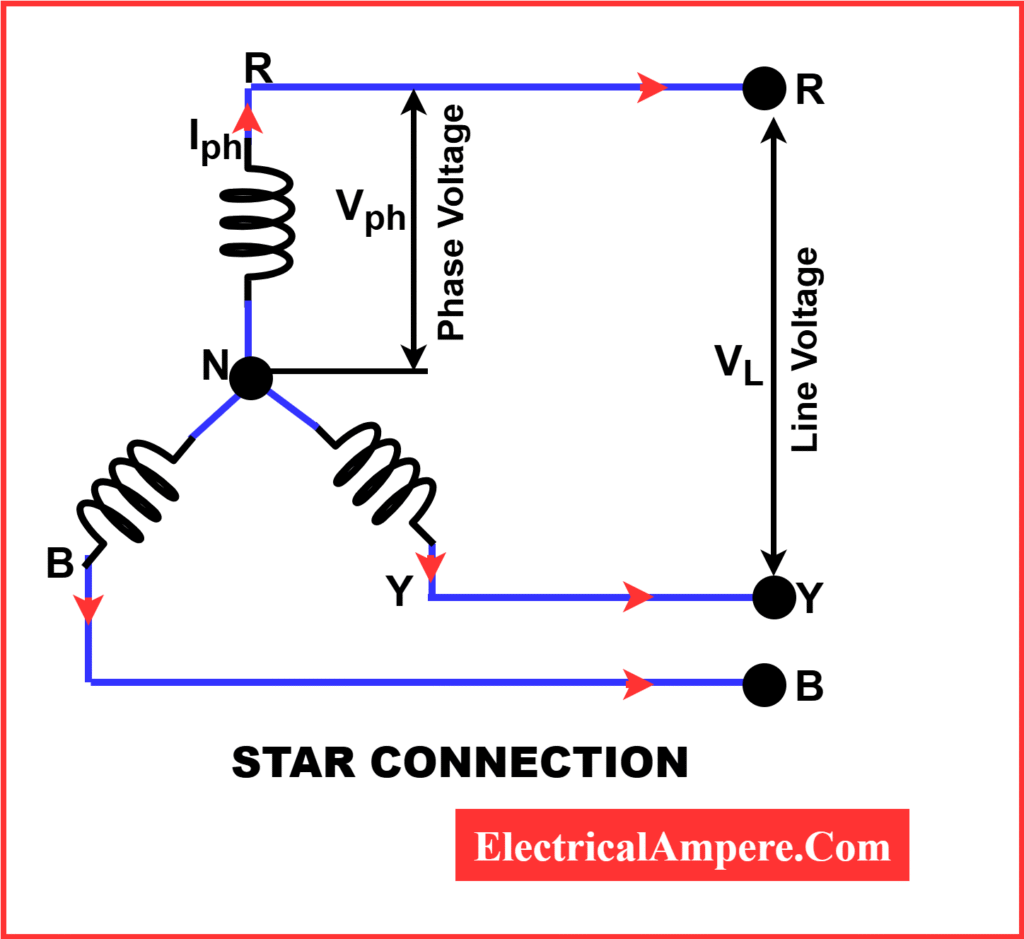
In this setup:
- Phase voltage (VPh) is the voltage across each winding.
- Line voltage (VL) is the voltage between any two lines.
Here’s a simple relationship that applies:
Line Voltage = √3 × Phase Voltage
Line Current = Phase Current
This configuration ensures that even at high line voltages, each winding handles a lower phase voltage, which reduces insulation requirements.
Example:
Suppose the line voltage in a star connection is 400V.
Then the phase voltage will be:
VPh = VL / √3
VPh = 400 / 1.732 ≈ 230V
So, although the system operates at 400V between lines, each winding only experiences 230V, significantly lowering the insulation needed for the equipment.
How Star Connection Works in 3-Phase Systems
Each phase in a star three-phase connection carries current at a 120-degree phase difference. Because of this time separation, the neutral point helps balance the system. If one load varies from the others, the neutral wire allows unbalanced current to return safely, maintaining system stability.
As a result, power transmission becomes more reliable and less prone to voltage drops or fluctuations.
Applications of Star Connection in 3-Phase Systems
The three-phase star configuration appears in many essential components of power systems.
- Alternators in power stations use star-connected windings to generate high voltage at lower current levels.
- Power transmission and distribution networks rely on star-connected transformers to support both single-phase and three-phase loads.
- Star-delta motor starters reduce starting current by initially connecting in star before switching to delta.
- Residential electricity supply systems use the neutral in star configurations to deliver 230V single-phase power.
Key Advantages of Star Connection
Let’s explore the reasons why many systems prefer the three-phase star connection.
1. Neutral Wire Supports Versatile Supply
By providing a neutral point, the star connection enables both single-phase and three-phase loads. This makes it suitable for residential and industrial systems alike.
2. Reduced Insulation Needs
Since each winding only experiences the phase voltage (which is lower than the line voltage), insulation becomes simpler and more cost-effective.
3. Efficient for Long-Distance Transmission
By using star-connected transformers, high voltages and lower currents can be achieved, which makes power transmission over long distances more efficient.
4. Safer for Residential and Commercial Use
The Y connection makes it easy to derive 230V supply for homes from a standard 400V three-phase network, thanks to the neutral wire.
Star-Star Connection Diagram in Transformers
Engineers often use a star-star connection diagram when designing step-down or step-up transformers. In this arrangement, both primary and secondary windings use the star configuration.
This setup works well for:
- Low load conditions
- Rural power supply systems
- Grounding requirements on both primary and secondary sides
Using this configuration ensures minimal voltage imbalance and simplifies grounding.
Star vs Delta Connection: What’s the Difference?
Here’s a quick comparison between star and delta connections:
| Feature | Star Connection | Delta Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Neutral Wire | Available | Not available |
| Line Voltage | √3 × Phase Voltage | Equal to Phase Voltage |
| Current in Windings | Equal to Line Current | √3 × Line Current |
| Starting Current | Low (ideal for motors) | High |
| Insulation Requirement | Lower | Higher |
| Application | Alternators, Home supply | High power motors, industrial systems |
Conclusion
To summarize,the star connection 3 phase system offers an efficient, safe, and flexible solution for modern power networks. Its ability to offer a neutral wire, handle both balanced and unbalanced loads, and reduce insulation requirements makes it a go-to configuration for engineers worldwide.
Whether you’re working with power generation, motor control, or residential electricity, the three-phase star configuration remains a fundamental and highly practical approach. Understanding how it works not only strengthens your grasp of electrical systems but also empowers better design and troubleshooting decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A Y-connection in a three-phase system is a method of wiring where one end of each of the three windings is connected to a common neutral point, forming a “Y” shape. The other ends are connected to the line conductors. This setup allows for both single-phase and three-phase power distribution.
1. It provides a neutral wire for single-phase loads.
2. Requires less insulation due to lower phase voltage.
3. Safer and more efficient for residential use.
In a star connection:
Line Voltage (VL) = √3 × Phase Voltage (VPh)
The line voltage is higher than the phase voltage, which helps reduce insulation costs and enhances safety.
Star connections are used in:
Power generation alternators
Distribution transformers
Residential and commercial power supply
Star-delta motor starters
In a star (Y) configuration, one end of each winding is joined at a neutral point, supporting both single- and three-phase outputs with lower starting current and reduced insulation needs.
Delta configurations form a closed loop, have no neutral, and suit high-power motors needing higher torque.
Related Articles: