Learn about the speed regulation of DC motor, including its definition, formula, and comparison among different types of DC motors. Understand how motor speed changes under load and why good speed regulation is essential.
When a DC motor is subjected to load, its speed gradually decreases. This drop in speed is undesirable, especially in applications where a constant speed is critical. That’s where the concept of speed regulation of a DC motor becomes important.
Speed regulation refers to the difference between the no-load speed and full-load speed of the motor. A motor that maintains nearly constant speed under varying loads is said to have good speed regulation. In such cases, the speed difference is minimal.
What is the Speed of a DC Motor?
The speed of a DC motor refers to how fast the motor’s shaft rotates, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). In real-world applications, it’s important that a DC motor maintains a consistent speed, even if the load or supply voltage changes. This consistent performance is known as speed regulation of DC motor.
Speed of a DC Motor Formula
To better understand speed regulation, it’s important to begin with the speed of a DC motor formula:
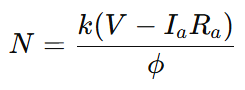
Where:
- N = Speed of the DC motor (in RPM)
- V = Supply voltage
- Ia = Armature current
- Ra = Armature resistance
- k= Motor constant (depends on construction and units)
- ϕ = Magnetic flux per pole
This is the dc motor speed formula used to calculate how fast a motor shaft rotates under various load conditions. It clearly shows that the speed of the motor is directly proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to the magnetic flux.
What is Speed Regulation of DC Motor?
Speed regulation is the measure of how much a motor’s speed changes between no-load and full-load conditions. Ideally, the speed of a DC motor should remain nearly constant under varying load conditions, especially in precision applications like robotics, fans, and electric vehicles.
Why Speed Regulation Matters
Good speed regulation ensures:
- Consistent performance
- Stable motor control
- Energy efficiency
- Reduced wear and tear
Motors with poor regulation slow down significantly under load, which can affect performance and damage the equipment.
Formula for Motor Speed Regulation
The speed regulation of a DC motor indicates how much the motor’s speed changes from no-load to full-load. It is an important performance metric that reflects how well a motor maintains its speed under varying load conditions.
Speed Regulation Formula (Per Unit Form)
In per unit (p.u.) system, the formula becomes:
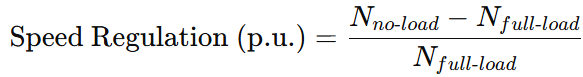
This gives a dimensionless ratio that simplifies comparison across different motors or systems. For example:
- A speed regulation of 0.05 p.u. means a 5% drop in speed under full-load conditions.
Speed Regulation Formula (Percentage Form)
The speed regulation of a DC motor is expressed as a percentage and calculated using the following formula:
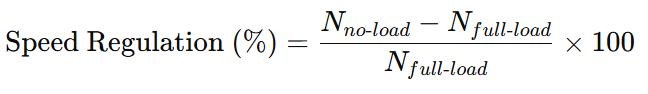
Where:
- Nno−load= Motor speed without any load
- Nfull−load = Motor speed under full load
A lower percentage indicates better speed regulation.
Example:
If a DC motor has:
- Nno-load=1550 RPM
- Nfull-load=1500 RPM
Then:
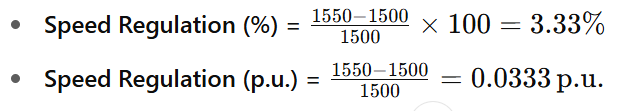
Speed Regulation of different Types of DC Motors
Let’s look at how different types of DC motors perform in terms of speed regulation:
| Type of DC Motor | Speed Regulation | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Permanent Magnet DC Motor | 10% – 15% | Good speed regulation |
| DC Shunt Motor | < 10% | Better speed stability |
| DC Series Motor | Poor | Significant speed drop with increasing load |
| DC Cumulative Compound Motor | ~25% | Less suitable for constant-speed applications |
| DC Differential Compound Motor | ~5% | Excellent for applications requiring consistent speed |
A lower percentage of speed regulation indicates a motor’s ability to maintain stable speed, even with changes in load. Among all, the DC differential compound motor stands out for its exceptional speed consistency.
Factors Affecting DC Motor Speed
Several elements influence the speed of DC motor:
- Supply Voltage (V): Higher voltage increases speed.
- Armature Resistance (Ra): Higher resistance reduces speed.
- Load on Motor: Heavier loads tend to slow the motor down.
- Magnetic Flux (φ): Stronger flux slows the speed; weaker flux increases it.
How to Improve Speed Regulation of DC Motors
- Use motors with good design (like shunt motors).
- Employ electronic speed controllers.
- Maintain constant load conditions.
- Ensure stable voltage supply.
- Use feedback systems (like tachometers).
Conclusion
The speed regulation of DC motor is a critical parameter that defines how well a motor maintains speed under changing loads. By understanding the speed of a DC motor formula and what factors influence motor performance, engineers and technicians can select or design motors that ensure efficiency and reliability in various applications.
For anyone working with electric drives, automation, or robotics, understanding of the dc motor speed formula and regulation techniques ensures that your systems operate smoothly and safely.
Read Next: