Disc insulator is a critical component in electrical power systems. It support and electrically isolate high-voltage conductors from transmission towers or poles, preventing leakage currents and ensuring safe power distribution. In this article, we provide a detailed guide on disc insulator types, uses, applications, and advantages to help you understand their significance in electrical networks.
What is a Disc Insulator?
A disc insulator (sometimes referred to as a disk type insulator) is a mechanical and electrical device used in overhead power lines. It is designed to:
- Support the weight of conductors
- Insulate the conductor from the supporting tower
- Withstand environmental conditions like rain, dust, and pollution
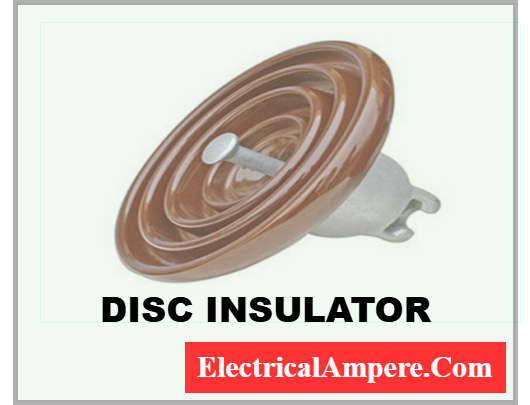

Materials Used in Disc Type Insulators
Disc insulators are manufactured from materials that provide high electrical resistance and mechanical strength:
- Porcelain – Durable, resistant to heat, moisture, and aging. Widely used in transmission and substation applications.
- Glass – Transparent, easy to inspect for cracks, high mechanical strength, and resistant to environmental wear.
- Polymer/Composite – Lightweight, vandal-resistant, and less prone to contamination effects.
Types of Disc Insulators
Disc insulators are classified based on design, material, and application. Broadly, they include Suspension Type and Strain Type insulators:
1. Suspension Type Insulator
- In a suspension insulator, the conductor hangs under the support point.
- Available in two forms:
- Connected Cap Type
- Interlinking (Hewlett) Type
- Advantages:
- More flexible and reliable than pin-type insulators
- Low cost compared to pin-type insulators
- Common applications in high-voltage transmission lines, with multiple discs connected in a string configuration to handle higher voltages.
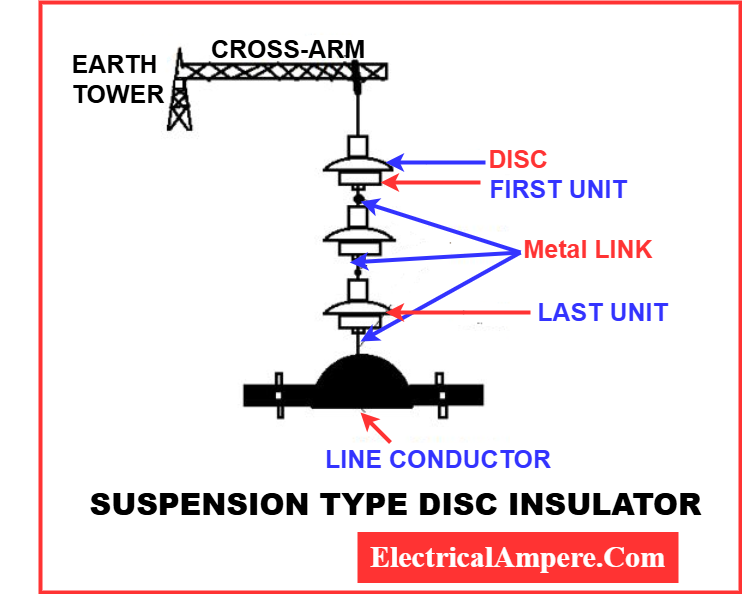
Read detailed artcile on: Suspension Type Insulator – Diagram, Types & Advantages
2. Strain Type Insulator (Tension Insulator)
- Also called tension insulator, used to handle mechanical tension in overhead lines.
- Discs are connected in a horizontal position, often in parallel strings for long spans.
- Two strings are connected through two yokes for stability.
- Widely used for:
- Supporting overhead power lines
- Radio antennas
- Applications requiring strong mechanical support under tension
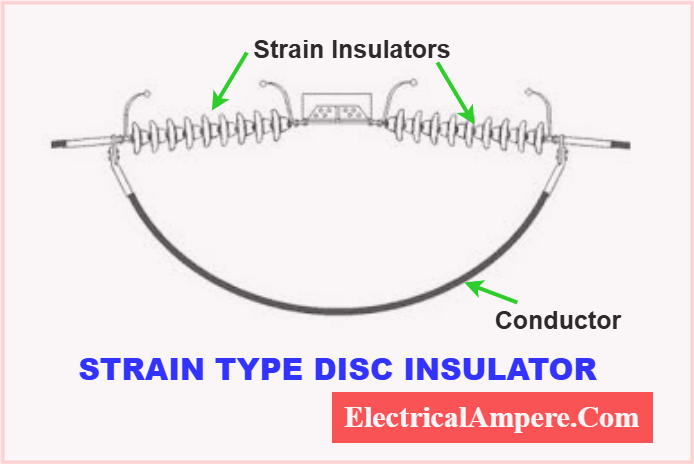
Material-Based Types (Additional Classification)
- Glass Disc Insulator – High mechanical strength, easy to inspect cracks
- Porcelain Disc Insulator – Durable and resistant to aging, ideal for transmission and substation use
- Polymer Disc Insulator – Lightweight, vandal-resistant, and low-maintenance
Uses of Disc Type Insulators
Disc insulators play an essential role in power transmission systems. Their primary uses include:
- Supporting Transmission Lines – They hold overhead conductors on transmission towers securely.
- Electrical Isolation – Prevents undesired current flow from conductors to the support structure.
- High Voltage Applications – By stringing multiple disc insulators, ultra-high voltage lines can be safely supported.
- Pollution Resistance – Protects conductors from leakage currents in areas with dust, industrial pollution, or coastal environments.
- Railway Electrification – Supports overhead wires, ensuring the safety and efficiency of railway electrification systems.
Applications of Disc Insulators
Disc type insulator is widely used across electrical networks for safe and efficient power transmission:
| Application Area | Purpose |
| High Voltage Transmission Lines | Insulates and supports conductors over long spans. |
| Substations | Ensures equipment is isolated and prevents short circuits. |
| Railways | Supports overhead catenary wires safely. |
| Industrial Power Systems | Provides insulation in high-voltage equipment for factories and plants. |
| Renewable Energy Plants | Used in wind and solar power transmission to handle high voltages efficiently. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Disc Insulators
Advantages
- Can handle normal voltage ratings like 11 kV, allowing suspension strings to be designed with multiple discs.
- In a suspension string, if a disc is damaged, it can be replaced individually.
- Mechanical stresses are reduced due to the elastic suspension of the hanging line.
- Can be used for any high voltage by connecting discs in a string.
- Repair is cost-effective, as only the damaged unit needs replacement.
- Protects from noise, electricity leakage, and heat.
- Provides reliable support to overhead conductors.
- In substations, it protects equipment like transformers and switchgear.
Disadvantages
- Suspension strings are more expensive than post and pin type insulators.
- Requires taller supporting structures to maintain safe ground clearance.
- Needs long cross-arms for proper installation.
- Towers must have higher weight capacity to withstand the insulator and conductor load.
How Disc Insulators Are Installed
- Disc insulators are often connected in series to form a string, increasing their voltage withstand capacity.
- Each insulator disc is attached to the tower and linked with a conductor.
- The number of discs in a string depends on line voltage, environmental conditions, and safety standards.
Disc Insulator vs Other Insulator Types
| Feature | Disc Insulator | Pin Insulator | Post Insulator |
| Shape | Circular disc | Cylindrical with groove | Cylindrical/rectangular post |
| Voltage Range | High voltage (>11 kV) | Low to medium voltage | Medium to high voltage |
| Material | Porcelain, Glass, Polymer | Porcelain, Glass | Porcelain, Polymer |
| Maintenance | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
| Applications | Transmission lines | Distribution lines | Substations & compact setups |
Conclusion
Disc insulators, including suspension and strain types, are vital for safe, efficient, and reliable power transmission. Whether glass, porcelain, or polymer, they provide both mechanical support and electrical insulation for high-voltage lines. Understanding disc insulator types, uses, applications, advantages, and limitations helps engineers, electricians, and planners ensure optimal performance of electrical networks.
For a complete overview, check out our Types of Insulators in Transmission Line guide.
Related Articles:
- Conductors and Insulators – Examples, Definition
- Stay Insulator: Definition,Types, Working Principle, Material
- What is Post Insulator? Types & Applications
- Strain Insulator- Definition, Construction, Working, Types, Applications
- Pin Type Insulator (Pin Insulator): Construction, Uses, Diagram & Advantages
- Suspension Type Insulator – Diagram, Types & Advantages
- What is Shackle Insulator: Working & Its Applications
- Types of Insulators Used in Overhead Transmission Line