A stay insulator prevents leakage current through guy wires in overhead lines. Learn its function, material, working principle, and how to choose the right manufacturer.
What is a Stay Insulator?
A stay insulator, also known as a guy strain insulator, is a non-conductive device used in stay wires (guy wires) to prevent the flow of leakage current to the ground. It is typically installed on the lower end of the stay wire, between the pole and the anchor point.
Its main function is to electrically isolate the live conductor systems from the ground, especially in case of fault conditions or voltage surges. This helps protect people, property, and animals from accidental electric shock.
Stay Insulator Diagram
The following diagram shows a typical installation of a stay insulator on a guy wire, positioned 8 feet above the ground between the pole and the anchor point.”
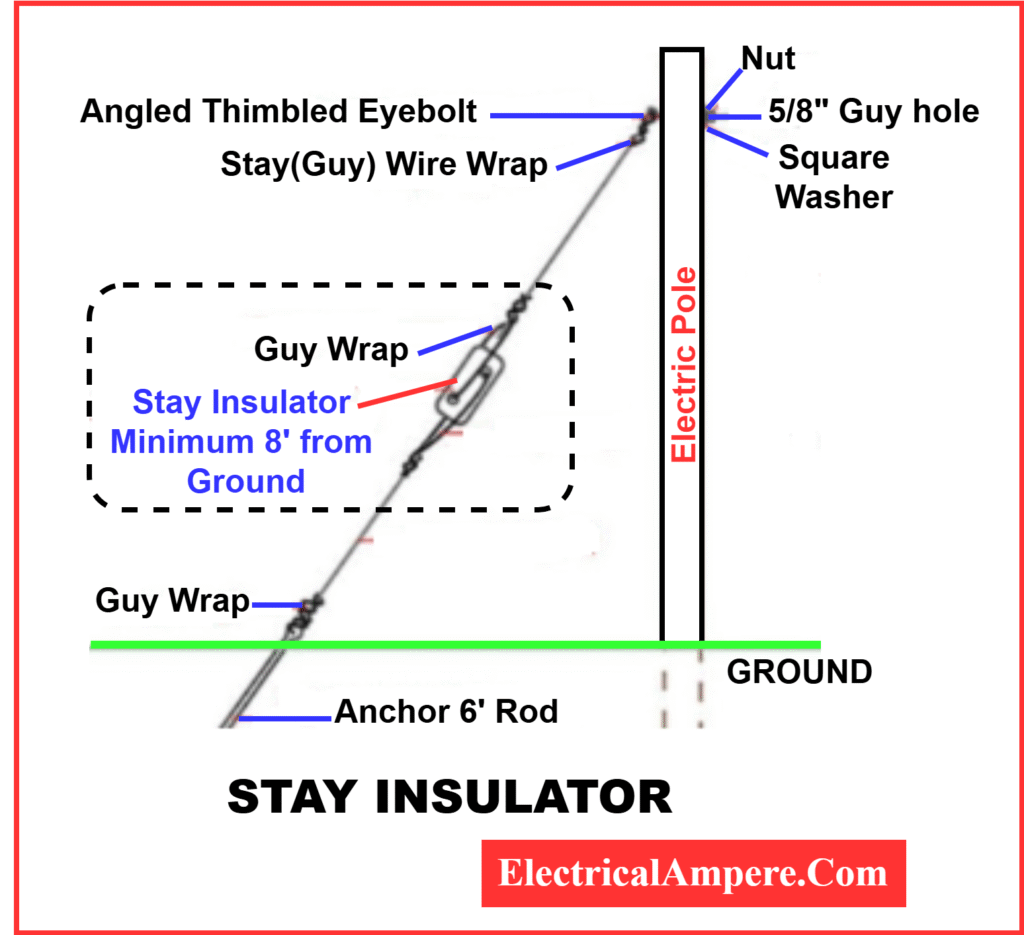
Working Principle of Stay Insulator
A stay insulator breaks the electrical continuity in a guy wire using a non-conductive material. It ensures mechanical strength while providing electrical isolation between the grounded portion and the energized part of the system.
During normal conditions, the guy wire remains under mechanical tension. If a fault or leakage current attempts to flow through it (due to a flashover or broken insulator), the stay insulator blocks the current path, protecting ground-level structures and living beings from electric shock.
Key functions:
- Provides electrical insulation between live and grounded parts
- Withstands mechanical load of the stay wire
- Prevents fault current from reaching earth through the guy wire
- Ensures safe operation of overhead distribution lines
What Material is Used in Stay Insulators?
Stay insulators are typically made from non-conductive, high-strength materials that can withstand outdoor conditions. Common materials include:
- Porcelain – the most widely used material due to its high mechanical strength and durability.
- Polymer/Composite materials – increasingly used in modern systems for their lightweight and impact resistance.
- Glass – occasionally used, but less common in stay insulators compared to suspension insulators.
These materials offer excellent dielectric strength and weather resistance, which are essential for outdoor applications.
Types of Stay Insulators
Different types are used based on mechanical load, voltage level, and site conditions. Below are the most common varieties:
1. Egg-Type
This oval-shaped insulator is the most common in low- and medium-voltage overhead lines. It provides electrical isolation in the stay wire and resists tension effectively.
2. Disc-Type
Disc-shaped variants are used where higher mechanical stress is expected. Their robust build supports longer spans or steeper angles in guy wire arrangements.
3. Polymer-Based
Lightweight and impact-resistant, these insulators are increasingly used in modern lines. They offer high dielectric strength and are suitable for areas prone to vandalism or contamination.
Key Benefits of Stay Insulators
The key advantages of installing a stay insulator include:
- Electrical isolation: Prevents the stay wire from becoming a path for electrical current.
- Safety: Protects linemen, pedestrians, and animals from potential electric shock.
- System reliability: Avoids unintentional grounding that could trip breakers or cause fault currents.
- Compliance: Helps meet regulatory safety standards in power distribution networks.
Technical Specifications of Stay Insulators
The table below shows key technical specifications of this type of insulator, including its mechanical strength, materials used, and relevant standards.
| Parameter | Value Range |
| Mechanical Strength | 5–10 kN |
| Material | Porcelain / Polymer |
| Creepage Distance | 200–300 mm |
| Standards Followed | IS: 5300, IEC 60383 |
Comparison Table: Stay Insulator vs Strain Insulator
These insulators may look similar but serve different functions. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Stay Insulator | Strain Insulator |
| Placement | On guy wires | Between conductors |
| Function | Electrical isolation | Mechanical tension handling |
| Material | Porcelain, Polymer | Porcelain, Glass |
| Common Application | Stay/guy wires of poles | Tension points in conductors |
Installation Procedure of Stay Insulator
Proper installation of a stay insulator is critical for ensuring electrical safety and mechanical reliability. Follow the steps below:
- Site Preparation
- Ensure the pole and guy anchor are securely positioned.
- Check the stay wire for correct tension and alignment.
- Determine Location
- Mark the position where the insulator will be installed (typically 1.5 to 2 meters above the ground anchor).
- In some cases, a second insulator may be installed near the top of the stay wire for added safety.
- Disconnect the Stay Wire
- Detach the guy wire from the anchor or pole end using appropriate safety tools.
- Use a temporary support to hold the wire in tension.
- Attach the Insulator
- Insert the stay insulator in line with the guy wire using shackles or wire loops.
- Ensure the correct orientation of the insulator if specified by the manufacturer.
- Secure Connections
- Fasten the guy wire ends tightly to both ends of the insulator.
- Double-check for mechanical stability and proper insulation clearance.
- Inspection and Testing
- Inspect for cracks or misalignments.
- Measure guy wire tension to confirm mechanical strength.
- Test for continuity to ensure proper electrical isolation.
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and local electrical safety standards (e.g., IS: 5300 or IEC 60383) during installation.
How to Choose the Right Stay Insulator Manufacturer in India
When selecting a stay insulator supplier, consider the following factors:
- IS/IEC certification for quality and standards compliance.
- Proven mechanical and electrical test results.
- Manufacturer’s experience in power utility components.
- Warranty and after-sales support.
- Timely delivery and bulk availability.
Notable Indian manufacturers include:
- BHEL – Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
- Elmex Controls Pvt. Ltd.
- Raychem RPG
- Shriram Insulators
- W.S. Industries
Applications of Stay Insulators
- Rural and urban power distribution networks
- Telecom poles with guy wires
- Electrified railway poles
- Coastal or polluted zones with high leakage risk
Conclusion
A stay insulator may look simple, but its function in an overhead line setup is indispensable. It ensures safety, insulation, and compliance, all while withstanding mechanical stress. Whether you’re designing a new line or replacing an old system, investing in quality stay insulators is a small cost for a big improvement in grid reliability.
Always verify the insulator’s mechanical test rating and material certification before bulk procurement to ensure long-term performance.
Related Articles: