Explore various cable tray types and sizes for electrical installations. Learn about ladder, perforated, solid-bottom, wire mesh, and channel trays in this complete guide.
What is Cable Tray Systems?
An electrical cable tray is a type of containment system used to support insulated electrical cables for power distribution, control, and communication. Today, electrical cable trays have become an essential component in industrial and commercial construction, providing a quick, economical, and flexible solution for cable management.
These cable tray systems serve as efficient alternatives to traditional wireways and electrical conduits, which fully enclose cables. Designed to support and protect all types of wiring—including high-voltage power lines, control cables, telecommunication cables, and fiber optic cables—they ensure organized routing, easy access for maintenance, and improved safety across various applications.
Purpose of Cable Trays
The primary purpose of a cable tray system is to offer structured support for power and communication cables. They provide a robust platform for routing, protecting, and managing both power and signal cables. These systems make it easier to upgrade, expand, or reconfigure electrical and communication networks, particularly in commercial and industrial setups.
Most cable tray systems are open in design, allowing for efficient heat dissipation and simple access during maintenance or repair work. Typically mounted on walls or suspended from ceilings, some systems are also suitable for underfloor installations.
Cable Tray Types
Choosing the right cable tray type is essential and is usually specified by an engineer or project designer. The selection depends on several factors such as the number of cables, cable weight, spacing, installation environment, and specific project needs.
Below are the most commonly used types of cable trays:
- Ladder-type
- Perforated type
- Solid bottom type
- Wire mesh
- Channel type
1. Ladder Cable Tray
The ladder-type cable tray is designed with two long side rails that are connected by evenly spaced rungs, resembling a ladder. This structure is especially useful for supporting heavy-duty cables over long distances. It allows for excellent ventilation around the cables, which helps in dissipating heat generated by electrical loads.

Additionally, the open design makes it easy to fasten or tie down cables securely at any point, simplifying both installation and maintenance. This type of tray is widely used in industrial settings where durability and cable accessibility are essential.
2. Perforated Cable Tray
The perforated cable tray features a flat bottom surface with numerous ventilation holes, along with raised side rails for added support. This design allows air to circulate freely around the cables, helping to reduce heat buildup and maintain safe operating temperatures. It is commonly used for supporting moderate cable loads in commercial and industrial installations.

The perforated base not only improves airflow but also offers better support and protection for the cables compared to open-style trays. This makes it a suitable choice for power distribution, control wiring, and communication cables.
3. Solid-Bottom Cable Tray
The solid-bottom cable tray is designed as a fully enclosed structure without any ventilation holes. This closed design provides complete coverage for the cables, making it an ideal choice for installations involving fiber optic cables and other sensitive signal cables.
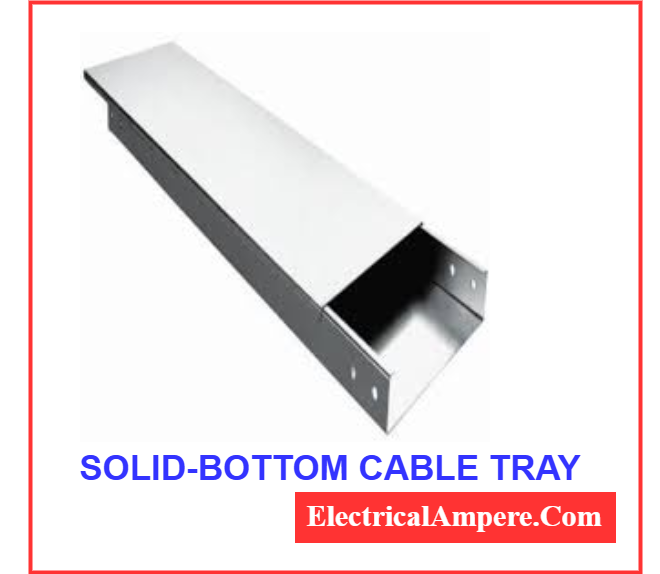

One of its key advantages is its ability to shield cables from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which can disrupt signal transmission. Additionally, the enclosed design protects the cables from dust, dirt, and moisture, ensuring a clean and secure environment for critical cabling systems.
4. Wire Mesh Cable Tray (Basket Tray)
The wire mesh cable tray, also known as a basket cable tray, is constructed using welded steel wires that form a mesh-like, open structure. This design is especially popular in data centers and telecommunications facilities due to its lightweight build and high flexibility.
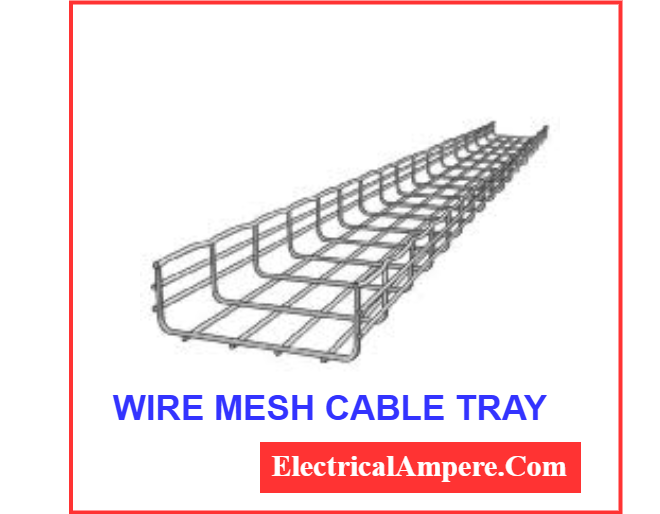

The open mesh allows for excellent air circulation, which helps in cooling the cables, and makes it easy to view, route, and manage cable paths. One of the major perks of this tray type is its ease of installation—cables can be laid in or removed from the tray quickly, making it ideal for environments where frequent changes or upgrades to the cabling system are expected.
They are best suited for low voltage, telecommunication, and fiber optic cables and are ideal for short-span applications.
5. Channel Cable Tray
The channel cable tray features a simple, U-shaped or channel-like structure that provides a compact and straightforward solution for supporting electrical cables. It is best suited for light cable loads and is often used in tight or confined spaces where larger tray systems may not fit.
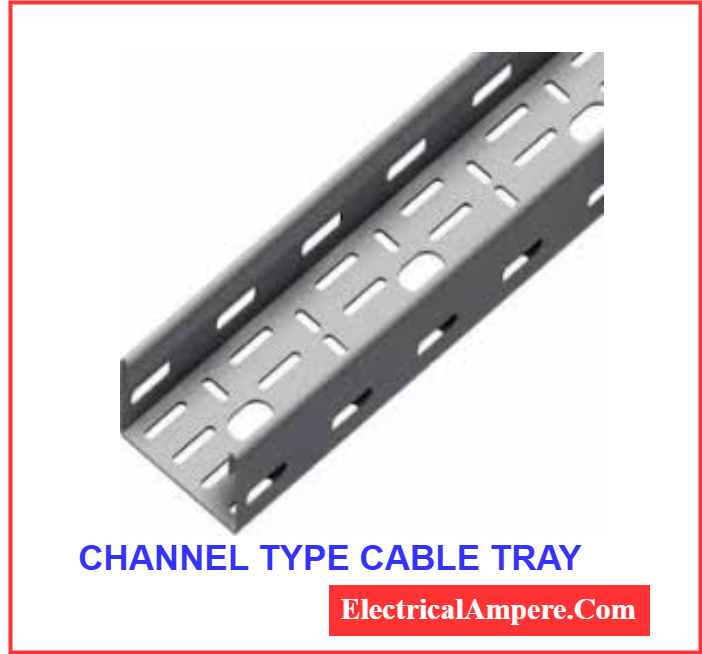
This type of tray is particularly useful for short cable runs and is commonly installed in small commercial or residential projects. One of its main advantages is that it is both compact and cost-effective, making it a practical choice for installations that require minimal support with limited space.
All these types of trays are available in various materials like aluminum, steel, stainless steel, and fiberglass, depending on environmental conditions and application demands.
Applications of Different Electrical Cable Tray Types
- Ladder trays: Power distribution, industrial plants
- Perforated trays: Commercial buildings, HVAC control wiring
- Solid-bottom trays: Data centers, fiber optic networks
- Wire mesh trays: IT infrastructure, hospitals, telecom
- Channel trays: Residential, small offices
Cable Tray Materials
Cable trays are available in both metallic and non-metallic materials:
1. Metallic
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant; ideal for most environments.
- Steel: Offers good electromagnetic shielding and strength.
- Stainless Steel: Excellent for high-temperature and corrosive environments.
2. Non-Metallic
- Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP): Nonconductive, corrosion-resistant, and lightweight, suitable for chemical or wet areas.
Precautions When Using Cable Trays
- Ensure proper bend radius, especially for fiber optic and coaxial cables, to avoid signal loss.
- Regular cleaning is crucial to prevent the buildup of combustible dust or clutter, especially in industrial settings.
Advantages of Cable Tray Systems
- Cost-Effective: Cheaper than enclosed conduit systems.
- Easy Maintenance: Cables are visible and accessible, making repairs or replacements easier.
- Safe: Regular inspection improves safety, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
Disadvantages
- Moisture Accumulation: Solid-bottom trays can trap moisture, which may affect cable performance if not properly managed.
Cable Tray Sizes
Choosing the right cable tray sizes and types depends on several factors such as:
- Number and size of cables
- Load capacity
- Spacing of supports
- Environmental conditions (indoor, outdoor, corrosive)
Standard Cable Tray Sizes (Width x Height):
- 50 mm x 25 mm
- 100 mm x 50 mm
- 150 mm x 75 mm
- 300 mm x 100 mm
- 600 mm x 150 mm
These are available in lengths of 2.5m, 3m, or 6m depending on regional standards.
Note: Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications or engineering standards for your region.
Conclusion
Understanding different cable tray types and matching them with the correct cable tray sizes is key to a successful electrical infrastructure. Whether it’s about load requirements or environmental factors, having knowledge of the types of electrical cable tray systems ensures better performance, reduced downtime, and simplified cable management.
By exploring trays types, and technical specifications, you can make an informed choice that balances safety, efficiency, and cost.

Read Next: