Use our KW to Amps Calculator to quickly and accurately convert kilowatts (KW) to amperes (A) for single-phase, and three-phase circuits. Fast, easy, and reliable!
Understanding the relationship between kilowatts (kW) and amperes (A) is crucial in electrical engineering, home installations, and industrial setups. A KW to Ampere Calculator helps simplify this conversion and ensures safety and accuracy in electrical design. Whether you’re sizing a circuit breaker or choosing the right wire gauge, knowing how to convert kW into amperes is essential.
What is KW?
kW (kilowatt) is a unit of electrical power that equals 1,000 watts. In electrical systems, it represents the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or generated.
What is Ampere?
Ampere (A) is the SI unit of electric current. It measures the amount of electric charge (electrons) flowing past a point in a circuit per second. One ampere is defined as one coulomb of charge passing through a point in one second.
What is a KW to Ampere Calculator?
A KW to Amps Calculator is a tool that allows you to convert kilowatts (kW) to amperes (A) based on the type of electrical system (single-phase or three-phase) and the voltage level.
The formula used depends on whether the system is:
- Single-phase AC
- Three-phase AC
- DC (Direct Current)
This tool is vital for electricians, engineers, and DIY enthusiasts to perform accurate kw to amps calculations safely.
KW into Amps Formula
Let’s break down how to calculate current from power:
For Single-phase AC:
To convert kilowatts (kW) to amperes (A) for single-phase alternating current (AC), multiply the power in kilowatts by 1000, then divide by the product of the power factor (PF) and the RMS voltage (V). The formula is:
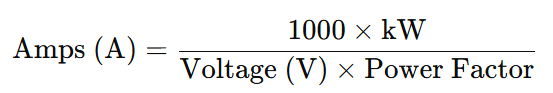
This calculation shows that the current depends on the power, voltage, and power factor in a single-phase AC system.
For Three-phase AC:
To convert kilowatts (kW) to amps (A) for a three-phase AC system using line-to-line voltage, multiply the power in kilowatts by 1000, then divide by the product of √3, the power factor (PF), and the line-to-line RMS voltage (VL-L). The formula is:
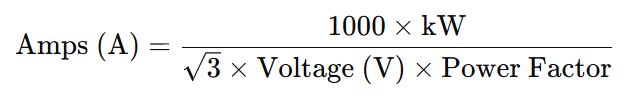
This formula is used when calculating current in three-phase systems with line-to-line voltage.
To convert kilowatts (kW) to amps (A) in a three-phase AC system using line-to-neutral voltage, multiply the power in kilowatts by 1000, then divide by the product of 3, the power factor (PF), and the line-to-neutral RMS voltage. The formula is:
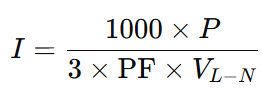
This method applies when calculating phase current using line-to-neutral voltage in a three-phase system.
For DC Circuits:
To convert kilowatts (kW) to amps (A) in a direct current (DC) system, multiply the power in kilowatts by 1000, then divide by the voltage in volts (V). The formula is:
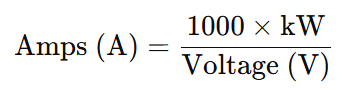
This means the current is directly proportional to the power and inversely proportional to the voltage.
Note: Power Factor (PF) typically ranges from 0.8 to 1 in practical applications.
KW to Amps Calculation Example
Let’s convert 5 kW to amps on a 230V single-phase system with a power factor of 0.9 Amps.
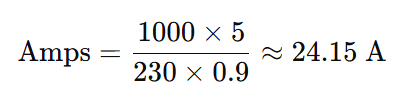
That means a 5 kW appliance would draw approximately 24.15 amperes.
Use Our KW to Amps Calculator Tool
Instead of manually crunching numbers, use a reliable kilowatts to amps calculator. Just input:
- Kilowatts (kW)
- Voltage (V)
- Power Factor (for AC systems)
- Phase Type (Single or Three-phase)
The tool instantly converts kw into amps saving time and ensuring accuracy.
Use the below calculator to find DC( Direct current)
Why Use a KW into Ampere Calculator?
- Kilowatts (kW) indicate the amount of power an electrical device consumes, while amperes (amps) measure the flow of electric current. Converting kW into amps is crucial for several practical reasons:
- Safe Wiring: Determining the correct wire size based on the kW load helps prevent overheating and reduces the risk of electrical fires.
- Circuit Breaker Selection: Knowing the current draw allows you to select a properly rated circuit breaker, ensuring the system isn’t overloaded or frequently tripping.
- Cost Estimation: By understanding how much current your equipment uses, you can better estimate electricity consumption and manage your energy expenses.
- Project Planning: Whether you’re designing a DIY solar power system or working on residential electrical installations, a kW to ampere calculator is an essential planning tool.
Typical Power Factor Values for Common Electrical Devices
The power factor (PF) of an electrical device indicates how effectively it uses electricity. A PF of 1.0 means all the power is being used effectively, while lower values indicate inefficiencies, usually due to reactive power. Below is a list of typical power factor values for various types of loads and equipment:
| Device / Load | Typical Power Factor |
|---|---|
| Incandescent Lamps | 1.0 |
| Resistive Loads (e.g., electric heaters, toasters) | 1.0 |
| Synchronous Motors | 0.8 – 0.95 |
| Small Induction Motors | 0.7 – 0.8 |
| Large Induction Motors | 0.85 – 0.95 |
| Transformers | 0.8 – 0.95 |
| Fluorescent Lighting (Magnetic Ballast) | 0.7 – 0.9 |
| Fluorescent Lighting (Electronic Ballast) | 0.9 – 0.99 |
| Computers and Electronic Devices | 0.6 – 0.8 |
| LED Lighting | 0.9 – 0.98 |
| Air Conditioners (Window or Split Units) | 0.8 – 0.95 |
| Industrial Welding Machines | 0.5 – 0.85 |
| Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) | 0.6 – 0.9 |
| Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) | 0.9 – 0.98 |
Important Note:
The power factor values listed above are approximate and may vary depending on the specific make, model, and operating conditions of the equipment. Factors like system load, age of the device, and the quality of electrical infrastructure can all impact the actual PF.
Conversion Table: Amps and Kilowatts for Three-Phase AC Supply
This table provides motor current ratings based on kilowatt (KW) output, assuming an efficiency of 0.8 and a power factor of 1. The values are calculated for a three-phase AC supply at the following voltages: 120V, 208V, 240V, 277V, and 480V.
| Power | Current (120V) | Current (208V) | Current (240V) | Current (277V) | Current (480V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1KW | 6.014A | 3.47A | 3.007A | 2.605A | 1.504A |
| 2KW | 12.028A | 6.939A | 6.014A | 5.211A | 3.007A |
| 3KW | 18.042A | 10.409A | 9.021A | 7.816A | 4.511A |
| 4KW | 24.056A | 13.879A | 12.028A | 10.421A | 6.014A |
| 5KW | 30.070A | 17.348A | 15.035A | 13.027A | 7.518A |
| 6KW | 36.084A | 20.818A | 18.042A | 15.632A | 9.021A |
| 7KW | 42.098A | 24.288A | 21.049A | 18.238A | 10.525A |
| 8KW | 48.113A | 27.757A | 24.056A | 20.843A | 12.028A |
| 9KW | 54.127A | 31.227A | 27.063A | 23.448A | 13.532A |
| 10KW | 60.141A | 34.697A | 30.070A | 26.054A | 15.035A |
| 15KW | 90.211A | 52.045A | 45.105A | 39.081A | 22.553A |
| 20KW | 120.28A | 69.393A | 60.141A | 52.107A | 30.070A |
| 25KW | 150.35A | 86.741A | 75.176A | 65.134A | 37.588A |
| 30KW | 180.42A | 104.09A | 90.211A | 78.161A | 45.105A |
| 35KW | 210.49A | 121.44A | 105.25A | 91.188A | 52.623A |
| 40KW | 240.56A | 138.79A | 120.28A | 104.21A | 60.141A |
| 45KW | 270.63A | 156.13A | 135.32A | 117.24A | 67.658A |
| 50KW | 300.7A | 173.48A | 150.35A | 130.27A | 75.176A |
| 55KW | 330.77A | 190.83A | 165.39A | 143.3A | 82.693A |
| 60KW | 360.84A | 208.18A | 180.42A | 156.32A | 90.211A |
| 65KW | 390.91A | 225.53A | 195.46A | 169.35A | 97.729A |
| 70KW | 420.98A | 242.88A | 210.49A | 182.38A | 105.25A |
| 75KW | 451.05A | 260.22A | 225.53A | 195.4A | 112.76A |
| 80KW | 481.13A | 277.57A | 240.56A | 208.43A | 120.28A |
| 85KW | 511.2A | 294.92A | 255.6A | 221.46A | 127.8A |
| 90KW | 541.27A | 312.27A | 270.63A | 234.48A | 135.32A |
| 95KW | 571.34A | 329.62A | 285.67A | 247.51A | 142.83A |
| 100KW | 601.41A | 346.97A | 300.7A | 260.54A | 150.35A |
| 125KW | 751.76A | 433.71A | 375.88A | 325.67A | 187.94A |
| 150KW | 902.11A | 520.45A | 451.05A | 390.81A | 225.53A |
| 175KW | 1,052.5A | 607.19A | 526.23A | 455.94A | 263.12A |
| 200KW | 1,202.8A | 693.93A | 601.41A | 521.07A | 300.7A |
| 225KW | 1,353.2A | 780.67A | 676.58A | 586.21A | 338.29A |
| 250KW | 1,503.5A | 867.41A | 751.76A | 651.34A | 375.88A |
| 275KW | 1,653.9A | 954.15A | 826.93A | 716.48A | 413.47A |
| 300KW | 1,804.2A | 1,040.9A | 902.11A | 781.61A | 451.05A |
| 325KW | 1,954.6A | 1,127.6A | 977.29A | 846.75A | 488.64A |
| 350KW | 2,104.9A | 1,214.4A | 1,052.5A | 911.88A | 526.23A |
| 375KW | 2,255.3A | 1,301.1A | 1,127.6A | 977.01A | 563.82A |
| 400KW | 2,405.6A | 1,387.9A | 1,202.8A | 1,042.1A | 601.41A |
| 425KW | 2,556A | 1,474.6A | 1,278A | 1,107.3A | 638.99A |
| 450KW | 2,706.3A | 1,561.3A | 1,353.2A | 1,172.4A | 676.58A |
| 475KW | 2,856.7A | 1,648.1A | 1,428.3A | 1,237.6A | 714.17A |
| 500KW | 3,007A | 1,734.8A | 1,503.5A | 1,302.7A | 751.76A |
| 525KW | 3,157.4A | 1,821.6A | 1,578.7A | 1,367.8A | 789.35A |
| 550KW | 3,307.7A | 1,908.3A | 1,653.9A | 1,433A | 826.93A |
| 575KW | 3,458.1A | 1,995.1A | 1,729A | 1,498.1A | 864.52A |
| 600KW | 3,608.4A | 2,081.8A | 1,804.2A | 1,563.2A | 902.11A |
| 625KW | 3,758.8A | 2,168.5A | 1,879.4A | 1,628.4A | 939.7A |
| 650KW | 3,909.1A | 2,255.3A | 1,954.6A | 1,693.5A | 977.29A |
| 675KW | 4,059.5A | 2,342A | 2,029.7A | 1,758.6A | 1,014.9A |
| 700KW | 4,209.8A | 2,428.8A | 2,104.9A | 1,823.8A | 1,052.5A |
| 725KW | 4,360.2A | 2,515.5A | 2,180.1A | 1,888.9A | 1,090A |
| 750KW | 4,510.5A | 2,602.2A | 2,255.3A | 1,954A | 1,127.6A |
| 775KW | 4,660.9A | 2,689A | 2,330.5A | 2,019.2A | 1,165.2A |
| 800KW | 4,811.3A | 2,775.7A | 2,405.6A | 2,084.3A | 1,202.8A |
Motor Current Ratings – Single-Phase AC Supply
Motor current ratings for a single-phase AC supply are calculated based on a 0.8 efficiency and a power factor of 1, with the ratings reflecting kilowatt (KW) output at 120V and 240V.
| Power | Current (120V) | Current (240V) |
|---|---|---|
| 1KW | 10.417A | 5.208A |
| 2KW | 20.833A | 10.417A |
| 3KW | 31.25A | 15.625A |
| 4KW | 41.667A | 20.833A |
| 5KW | 52.083A | 26.042A |
| 6KW | 62.5A | 31.25A |
| 7KW | 72.917A | 36.458A |
| 8KW | 83.333A | 41.667A |
| 9KW | 93.75A | 46.875A |
| 10KW | 104.17A | 52.083A |
| 15KW | 156.25A | 78.125A |
| 20KW | 208.33A | 104.17A |
| 25KW | 260.42A | 130.21A |
| 30KW | 312.5A | 156.25A |
| 35KW | 364.58A | 182.29A |
| 40KW | 416.67A | 208.33A |
| 45KW | 468.75A | 234.38A |
| 50KW | 520.83A | 260.42A |
| 55KW | 572.92A | 286.46A |
| 60KW | 625A | 312.5A |
| 65KW | 677.08A | 338.54A |
| 70KW | 729.17A | 364.58A |
| 75KW | 781.25A | 390.63A |
| 80KW | 833.33A | 416.67A |
| 85KW | 885.42A | 442.71A |
| 90KW | 937.5A | 468.75A |
| 95KW | 989.58A | 494.79A |
| 100KW | 1,041.7A | 520.83A |
| 125KW | 1,302.1A | 651.04A |
| 150KW | 1,562.5A | 781.25A |
| 175KW | 1,822.9A | 911.46A |
| 200KW | 2,083.3A | 1,041.7A |
| 225KW | 2,343.8A | 1,171.9A |
| 250KW | 2,604.2A | 1,302.1A |
| 275KW | 2,864.6A | 1,432.3A |
| 300KW | 3,125A | 1,562.5A |
| 325KW | 3,385.4A | 1,692.7A |
| 350KW | 3,645.8A | 1,822.9A |
| 375KW | 3,906.3A | 1,953.1A |
| 400KW | 4,166.7A | 2,083.3A |
| 425KW | 4,427.1A | 2,213.5A |
| 450KW | 4,687.5A | 2,343.8A |
| 475KW | 4,947.9A | 2,474A |
| 500KW | 5,208.3A | 2,604.2A |
| 525KW | 5,468.8A | 2,734.4A |
| 550KW | 5,729.2A | 2,864.6A |
| 575KW | 5,989.6A | 2,994.8A |
| 600KW | 6,250A | 3,125A |
| 625KW | 6,510.4A | 3,255.2A |
| 650KW | 6,770.8A | 3,385.4A |
| 675KW | 7,031.3A | 3,515.6A |
| 700KW | 7,291.7A | 3,645.8A |
| 725KW | 7,552.1A | 3,776A |
| 750KW | 7,812.5A | 3,906.3A |
| 775KW | 8,072.9A | 4,036.5A |
| 800KW | 8,333.3A | 4,166.7A |
| 825KW | 8,593.8A | 4,296.9A |
| 850KW | 8,854.2A | 4,427.1A |
| 875KW | 9,114.6A | 4,557.3A |
| 900KW | 9,375A | 4,687.5A |
| 925KW | 9,635.4A | 4,817.7A |
| 950KW | 9,895.8A | 4,947.9A |
| 975KW | 10,156A | 5,078.1A |
| 1000KW | 10,417A | 5,208.3A |
Convert KW to Amperes Table (Single-phase, PF = 1, 230V)
| Kilowatts (kW) | Amps (A) |
|---|---|
| 1 kW | 4.35 A |
| 2 kW | 8.70 A |
| 3 kW | 13.04 A |
| 5 kW | 21.74 A |
| 10 kW | 43.48 A |
For systems with different voltage or power factor, use a kw amps calculator.
FAQs – KW and Ampere Conversion
What is the power factor in KW to Amps conversion?
Power factor accounts for efficiency in AC circuits. It’s typically 0.8 to 1. A lower PF means more current for the same power.
Is the KW to Amps conversion different for 3-phase and single-phase?
Yes. Three-phase circuits involve √3 (approx. 1.732) in the formula and typically use less current for the same kW.
Can I use the same formula for DC systems?
DC systems are simpler. Just divide kW × 1000 by the voltage to get amperes.
Conclusion
The KW to Ampere Calculator is a must-have for anyone dealing with electrical loads. Whether you’re designing a new circuit or upgrading equipment, converting kw into amps correctly ensures safety and efficiency.
Read Next: