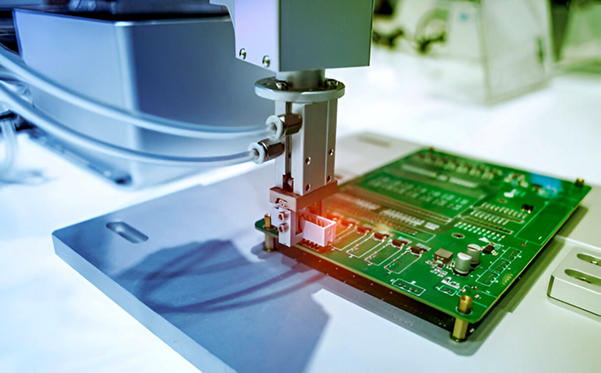
Printed Circuit Boards or PCBs have also greatly progressed in response to the escalating demand for electronics. We used to know PCBs as the rigid green boards with components on either the top or bottom side that can be found in many basic devices that we own such as phones, computers and home appliances. Now, PCBs are everywhere, serving various purposes such as for sensing, storing and controlling.
With the limitless power of technology, PCBs have also extensively evolved into various types such as flexible, multi-layered and doubled-sided types. The methods by which PCBs are fabricated and assembled have also advanced to adapt to this increasing complexity in design. The goal is not only to produce and assemble boards that meet the intended functional performance but also to minimise the cost.
In this article, we will dwell on the discussion of the costs involved in double sided PCB assembly,
What is a Double-Sided PCB?
A double-sided PCB is a type of PCB where the top and bottom portions of PCBs are utilized for component mounting. It consists of conductive patterns on both sides of the boards to make component mounting or attachment possible. The assembly of double-side PCB is applicable for rigid, flexible and rigid-flex types of printed circuit boards. Design rules and assembly guidelines exist for double sided PCB assembly for more robust processing. For instance, some components should not be placed on the opposite side of each other due to potential early fatigue failure of solder joints.
What are the Steps Involved in Double-Sided PCB Assembly?
Double sided PCB assembly has two method classifications. The first one is the conventional Through Hole Technology or THT. In this method, the leads are inserted into the PCB holes taking up much more space due to the drilled and plated holes. The second method is known as Surface Mount Technology or SMT.
- Solder Paste Printing. The bare PCBs are printed with solder paste using a stencil and a squeegee. The stencil dimensions allow the correct volume to be distributed into the soldering pads.
- Component Pick and Place. After the paste has been printed into the PCB pads, the components are picked from the feeder and placed into their pre-programmed positions. A sophisticated vision system helps the machine locate the reference points to accurately position the electronic parts.
- Reflow. To achieve a fully cured solder between the components and the PCB, reflow is done using an oven with heating and cooling zones. The temperature settings are dictated by the solder specifications, PCB thickness and component density, thus, it is important to conduct evaluations to have an optimum reflow step.
- Inspection. In double-sided PCB assembly, automated optical inspection is done on each side of the PCB after completing one pass in the SMT line. X-ray inspection can be performed on either side depending on the criticality of the components attached to the PCB.
- Testing. After both sides of the PCBs have been mounted with components, testing is performed to detect open and short and check for chip resistor and inductor values. Testing is done using an In-Circuit Tester or ICT where probes come in contact with the test nodes to initiate the testing process.
Double-sided circuit board assembly will need to undergo the said steps twice for the second side of the board. Despite redoing the steps, parameters and program settings vary for the top and bottom sides of the board. For instance, the positions of the components are different and even the thermal mass will not be the same for the top and bottom sides.
What are the Costs Involved in Double-Sided PCB Assembly?
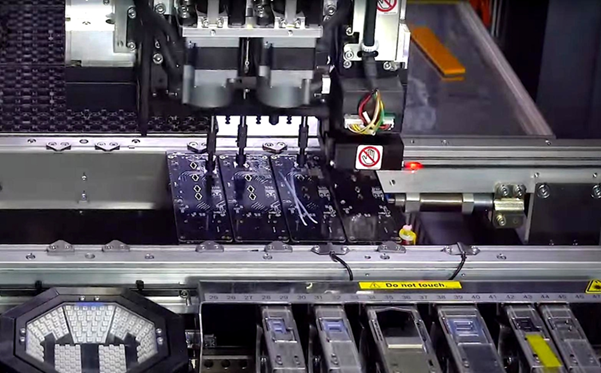
As we have deepened our understanding of the different processes in double sided PCB assembly, it will be easier to grasp the different cost factors that have to be considered.
- Number and Types of Components. The number of components directly impacts the cost of double-sided PCB. Denser boards will cost more due to the longer cycle time during chip placement and testing processes. Aside from the processing time, a higher amount of soldering material translates to higher costs.
- Type of Assembly. Recall that assembly processes are categorized through hole or surface mount technology only. SMT is generally considered cheaper and more beneficial for high-volume production due to its efficiency. The type of assembly to use must be understood as it contributes significantly to the cost of the PCB. In some cases, the double-sided circuit board assembly design can combine THT and SMT processes. This increases the complexity of the assembly process as selective wave soldering and component insertion steps are incorporated into the process flow of the PCB.
- Material Costs. Materials used in double-sided circuit board assembly include the components, soldering materials and the bare PCB substrates which play a huge part in the overall cost of double-sided PCB. The procurement team has the responsibility to find suppliers that will offer low prices while still meeting the quality and performance. In some business models, material purchasing is relied on a turnkey PCB assembly supplier while other customers would prefer to consign the materials.
- Jigs and Fixtures. Jigs and fixtures in double-sided printed circuit board assembly fall under Non-Recurring Engineering (NRE) expenses as these are one-time project costs. These include the carriers that will convey the PCBs toward the SMT machines, fixtures for the inspection and testing processes and other jigs required to achieve a hands-free and automated PCB assembly. The PCBs need to be held in place with a stable base to ensure accuracy during chip placement and soldering processes. Proper design and material choice of these specialized tools helps to reduce defects and promote robust manufacturing.
- Set-up and Programming Costs. Other costs in double-sided circuit board assembly that must be considered are set-up and programming costs. These are also classified under non-recurring engineering costs which are some initial costs incurred required to set up test and machine programs. Double-sided printed circuit board assembly will take longer to set up as it is more complex than single-sided PCB assembly. Engineering charges are added as programs must be written, developed and tested to determine if the PCB assembly will run smoothly during the production phase.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding the processes and cost factors involved in double-sided PCB assembly is essential for making informed production decisions. From component selection and assembly type to material procurement and specialized tooling, each aspect plays a vital role in determining overall expenses. For businesses seeking high-quality, cost-effective manufacturing, partnering with an experienced provider of PCB assembly services in China can offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency, scalability, and competitive pricing, ensuring that both performance and budget requirements are met.