Electric poles refer to various poles and towers used as support structures for overhead power line conductors. They are engineered to ensure safe and efficient electricity transmission across long distances. The electric pole is also known as an electric post and utility pole. Typically, electric poles have the following key characteristics:
- High mechanical Strength to support the weight of conductors and withstand additional stresses such as wind and other environmental forces.
- Lightweight and durable while maintaining the capacity to endure significant mechanical stress.
- Cost-effective in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Longer life
- Convenient access to conductors, simplifying inspection and repair tasks.
Wooden poles, concrete poles, steel poles, and rail poles are electric pole types used as support structures for overhead lines.
The choice of poles depends on factors such as the load’s significance, the location and terrain, the construction cost—including maintenance expenses—and the profitability of the project. For low-voltage lines, a single pole line is typically used to accommodate all phases, including earth and neutral. The electrical system utilizes various types of poles to support its different components.
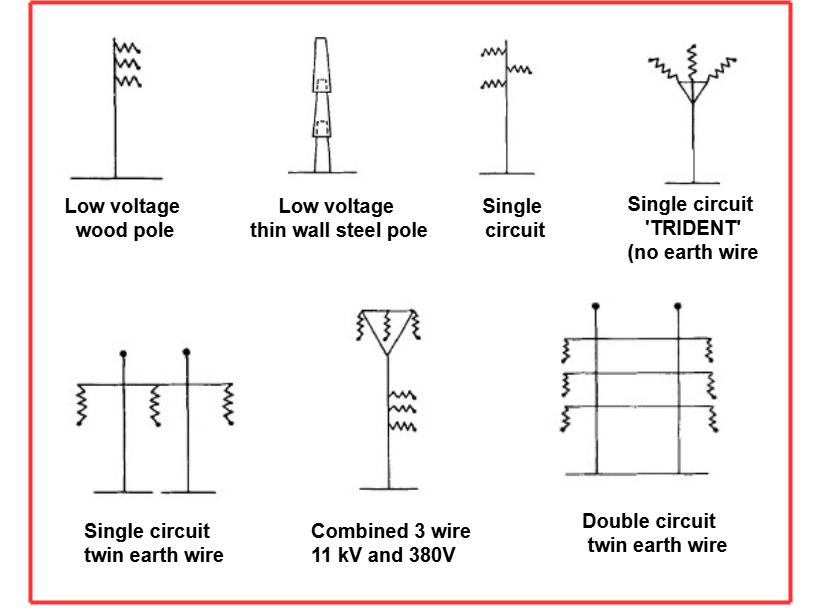
Types of Electric Pole
There are four main types of electric poles.
1). Wooden Electric Pole
2). Concrete Electric Pole
3). Steel Tubular Electric Pole
4). Rail Electric Pole
Wooden Electric Pole
A considerable amount of low-tension lines (400 volts and 230 volts) and high-tension lines (11 kilovolts) are supported by wooden poles. When necessary for the 33 KV line, use wooden poles at certain points . A wooden pole’s cost-effectiveness is substantially lower in comparison to that of any other electric pole, and the expenditure that has been made for its foundation is likewise relatively extremely low in comparison to other foundation costs. The wooden pole will remain in good condition for an extended length of time provided that it is properly maintained and treated.
Wooden poles are commonly used to support low-tension lines (400 volts and 230 volts) and high-tension lines (11 kilovolts). In certain cases, they are also utilized for 33 kV lines at specific locations. Compared to other types of electric poles, wooden poles are highly cost-effective because of much lower foundation expenses. With proper maintenance and treatment, wooden poles can remain in good condition for an extended period.
Wooden poles are classified into three distinct categories based on their ability to support the weight of electric cables.
- The breakdown force exceeds 850 kg/cm². Examples are Shaal, Masua wood, etc.
- The breakdown force ranges between 630 and 850 kg/cm². Examples are Tik, Seishun, Garjan wood, etc.
- The material fails under a force ranging from 450 to 630 kg/cm². Examples are Chir, Debdaru, Arjun wood. etc.
The wood selected for use in electric poles must be of high quality. Straight wood is highly recommended for this purpose. In exceptional cases, two shorter poles can be joined to meet the required length.

Wooden Pole Treatment
The first step in protecting wood is curing, which involves thoroughly drying it. Dry wood is essential because it reduces the risk of damage caused by mushrooms and termites, with termites being the most destructive. Heat and dampness are also significant threats to wood, especially in areas near or below ground level. To safeguard the wood from these issues, it is chemically treated. A mixture of tar with Creojet Oil or Copper Chromate Arsenic is commonly used for this purpose. This process, known as the Askew treatment, involves placing the wooden poles in a sealed cylindrical tank. Inside the tank, the poles are submerged in a Copper Chromate Arsenic solution. High pressure, up to 100 kilograms per square meter, is applied for at least one hour. This pressure forces the chemical deep into the wood’s pores, providing long-term protection against moisture and termites.
If the wood is not properly treated, the entire surface of the pole should be sprayed with two coats of Creojet oil before installation. Bituminous Creojet Oil should be applied to the part of the pole that will be in the soil and up to 50 cm (20 inches) above ground level. If this is not possible, tar should be applied to the pole’s surface. If neither of these treatments is feasible, the outer surface of the bottom two meters of the pole should be burned to protect it from termites and dampness.
The top of the pole should be shaped into a pointed cone to prevent water from accumulating. Necessary slots should then be cut in the top section to securely fit the cross arms. The diameter of the drilled holes should range from 17 mm to 20 mm. D-shaped iron clamp grooves are unnecessary; a bored hole at the required distance is sufficient. The distance between the top hole and the pole’s tip should be at least 200 mm (8 inches). All holes or grooves should be made before the treatment process. After treatment, creating new holes or grooves should be avoided. If it is necessary to make them post-treatment, they must be filled with creosote oil or bitumen for protection.
Concrete Electric Pole
Types of Concrete Electric Pole
There are two types of concrete poles:
1). P.C.C. Poles
1). P.C.C. Poles
Plain Cement Concrete poles (P.C.C. poles) are widely used in 11 KV and 400/230 volt systems and are also utilized in 33 KV high-tension (H.T.) lines. While PCC poles are more expensive than wooden poles, they are less costly than steel poles. They offer a longer lifespan and require minimal maintenance. The strength of a PCC pole is much greater than that of a wooden pole but lower than that of a steel pole. However, PCC poles have two main drawbacks: they are heavy and prone to breaking easily.

The cement concrete electric pole is made from cement concrete and reinforced with iron bars or rods to increase its strength. For earthing purposes, a 25 mm × 3 mm copper strip is embedded within the pole during concreting or a hollow channel is provided to insert the earthing wire. Additionally, 20 mm diameter holes are created in the pole during concreting to accommodate various fittings as required.
The cross-section of the pole is always wider at the bottom than at the top. For PCC poles, the cross-section is rectangular rather than square.
The height of electric poles varies depending on their type and application, which is crucial in determining their load-bearing capacity. Based on their height and lateral load capacity, concrete poles are divided into 11 classes.
| Pole classification | Height (Mtr) | Footing Deftness Excavation (Mtr) | Maximum Lateral Load (Kg2) |
| 1 | 16.5 m to 17 m | 2.40 | 3000 Kg2 |
| 2 | 16.5 m to 17 m | 2.40 | 2300 Kg2 |
| 3 | 16.5 m to 17 m | 2.40 | 1800 Kg2 |
| 4 | 16.5 m to 17 m | 2.40 | 1400 Kg2 |
| 5 | 14.5 m to 16 m | 2.30 | 1100 Kg2 |
| 6 | 11.5 m to 12 m | 2.00 | 1000 Kg2 |
| 7 | 11.5 m to 12 m | 2.00 | 800 Kg2 |
| 8 | 11.5 m to 12 m | 2.00 | 700 Kg2 |
| 9 | 9.5 m to 11 m | 1.80 | 450 Kg2 |
| 10 | 8 m to 9 m | 1.50 | 300 Kg2 |
| 11 | 6 m to 7.5 m | 1.20 | 200 Kg2 |
The excavation of footings depends on the soil conditions and differs from one location to another.
2). R.C.C. Poles
In recent years, reinforced concrete poles (R.C.C. Poles) have become a popular choice for line support. Compared to steel poles, they offer superior mechanical strength, a longer lifespan, and the capacity to support larger spans. Additionally, R.C.C. poles provide an aesthetically pleasing appearance, require minimal maintenance, and effectively insulate the surrounding area.

The perforations in the poles facilitate climbing and reduce the load that line supports need to bear. However, the primary challenge in using these poles is the high cost associated with transportation due to their heavyweight. To overcome this, such poles are often constructed on-site to minimize shipping expenses.
Steel Tubular Electric Pole
Steel tubular poles have significantly higher load-bearing capacity compared to wooden and concrete poles. With proper maintenance, these poles can have a longer lifespan. However, due to their high cost, their usage is gradually declining. Steel tubular poles are commonly used in low and medium voltage systems (400/230 volts) and are also employed in 11 kV H.T. lines. In some cases, such as for 33 kV systems, these poles are utilized.
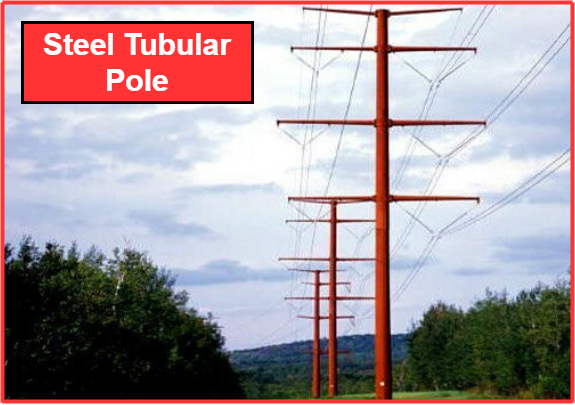
Types of Steel Tubular Electric Pole
Tubular poles are classified into two types:
1). Swaged Pole
2). Stepped Pole
1). Swaged Pole
Swaged Tubular Poles are constructed using high-grade raw materials such as MS steel and sheets throughout the manufacturing process. The swaging process, as opposed to simple linking, enhances their strength and stability. Due to the versatility of steel, these poles can be used in a wide range of applications across commercial, residential, and municipal sectors. Architects, engineers, and design professionals can effectively utilize them for various projects.

Installation times can be significantly reduced due to the product’s durability and strength, coupled with its lightweight and maintenance-free design, which minimizes shipping costs.
Swaged poles are made from high-quality tubes, either welded or seamless, which are cut to the required lengths before being swaged and joined. The term “swaged poles” encompasses various types of lighting fixtures, including single- and double-hanging light poles, traffic light poles, and street light poles.
ERW welded tubes are cut to the required lengths and then swaged and joined to form swaged poles.
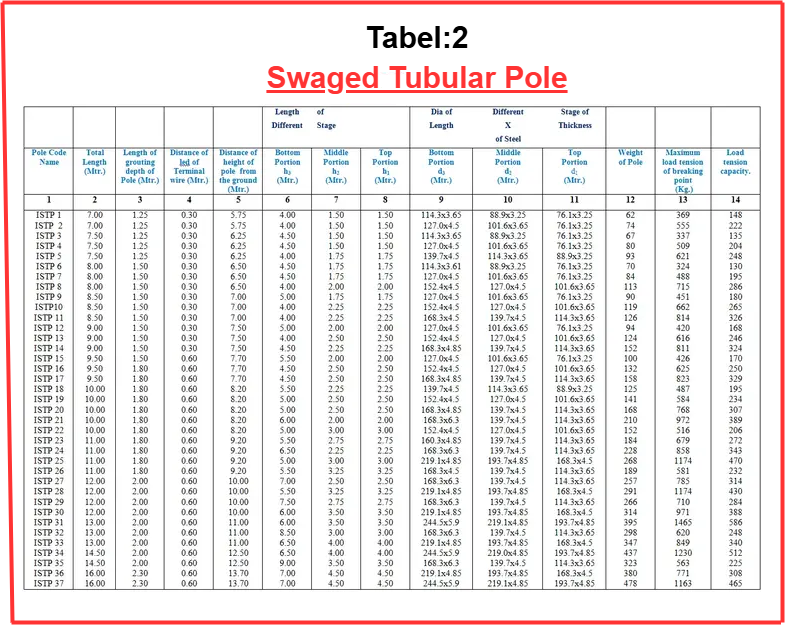
The safety factor of the pole is 2.5, and the weight of steel is 7.85 grams per square centimeter.
2). Stepped Pole
Stepped poles are produced using a unique hot-swaged joint technique. This process involves applying heat to larger-diameter pipes to fuse them with smaller-diameter pipes, creating extremely strong and durable pipe junctions.
The joints are completely sealed which allows the pole to maintain its strength along its entire length. Since there is no need for welding, the joints remain secure and reliable throughout the pole’s lifespan.
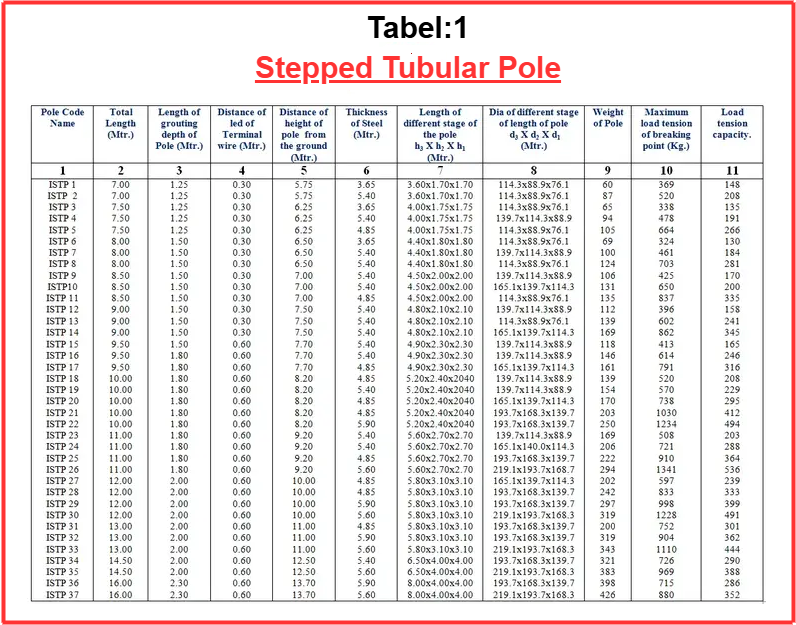
The safety factor of the pole is 2.5, and the weight of steel is 7.85 grams per square centimeter.
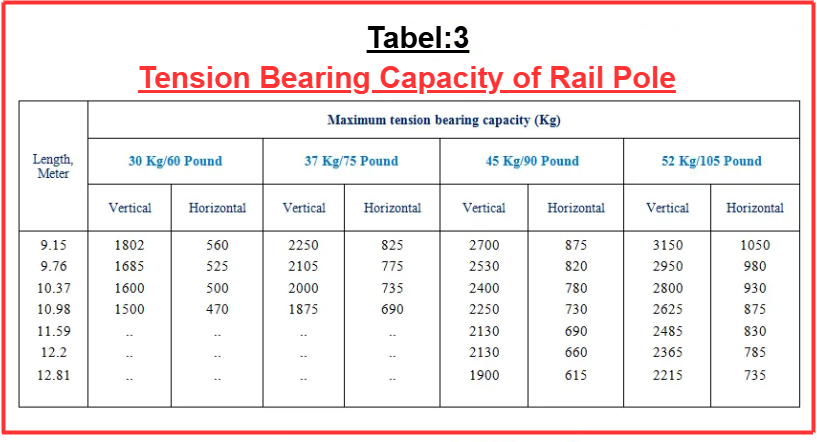
Rail Electric Pole
Rail poles offer the highest strength, but they come with the highest cost. Their increased weight also results in higher transportation, loading, and unloading expenses.
This pole is not suitable for lines operating at 400/230 volts. Rail poles are specifically used for 11 KV and 33 KV systems. The rail poles utilized in overhead lines are available in four different sizes.
- 30 kg/m
- 37 kg/m
- 45kg/m
- 52 kg/m

For 11 KV lines, we typically use 45 kg per meter rail poles, while for 33 KV lines, we use both 45 kg per meter and 52 kg per meter rail poles. The length of rail poles varies between 9 meters and 13 meters. Before installing a rail pole, we apply at least one coat of red oxide. To enhance the pole’s durability, a tar coat is applied to the bottom part of the pole up to a certain height above the ground. The vertical load-bearing capacity of the rail pole is higher than its horizontal load-bearing capacity.