A circuit breaker that uses pressurized SF6 gas to extinguish the arc is known as an SF6 circuit breaker. SF6 (Sulphur Hexaflauride) gas has outstanding dielectric, arc quenching, chemical, and physical properties, demonstrating its superiority over other arc quenching media, such as oil or air. The SF6 circuit breaker is primarily categorized into three types.
- Non-puffer piston circuit breaker
- Single-puffer piston circuit breaker.
- Double-puffer piston circuit breaker.
Air and oil were used as insulating mediums in circuit breakers. However, their arc extinguishing force was relatively slow after the contact separation movement. In contrast, high-voltage circuit breakers require quick arc extinction properties to enable swift voltage recovery. SF6 circuit breakers possess excellent properties, making them a preferred choice over oil or air circuit breakers. Therefore, SF6 circuit breakers are used for high voltages up to 760 kV.
Properties of Sulphur hexafluoride Circuit Breaker
Sulfur hexafluoride has excellent insulating and arc-quenching properties, making it highly desirable for electrical equipment and power systems.
- It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and non-inflammable gas.
- SF6 gas is a highly stable and inert gas with a five times greater density than air.
- It has a higher thermal conductivity than air, which helps cool current-carrying parts more efficiently.
- SF6 gas is highly electronegative; therefore, removing free electrons from discharge is easy by forming negative ions.
- It has the unique property of fast recombination after removing the source energizing spark, making it 100 times more effective than an arc quenching medium.
- Its dielectric strength is 2.5 times that of air. The gas dielectric strength increases at high pressure, although it is 30% less than dielectric oil.
- Moisture is very harmful to the SF6 circuit breaker. When the circuit breaker is interrupted, humidity and SF6 gas react in the presence of arc and form hydrogen fluoride, which can corrode the parts of the breaker.
Construction of SF6 Circuit Breakers
SF6 circuit breakers consist of two parts: the interrupter unit and the gas system.
Interrupter Unit – The Interrupter Unit comprises fixed and moving contacts, including parts that carry current and an arcing probe. This unit is connected to the SF6 gas reservoir, and it includes slide vents in the moving contacts that allow high-pressure gas to enter the main tank.
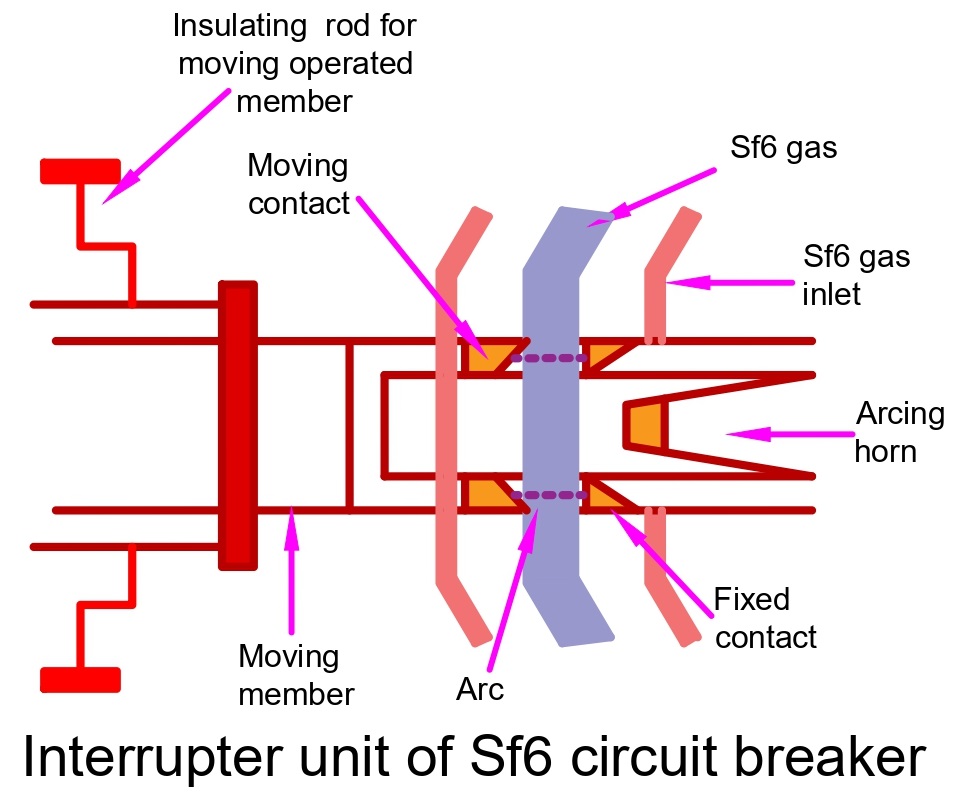
Gas System – SF6 circuit breakers use a closed-circuit gas system. Since SF6 gas is expensive, it is reclaimed after every operation. This system has two chambers – low-pressure and high-pressure – and includes a low-pressure alarm with warning switches. If the gas pressure becomes too low, the dielectric strength of gases decreases, and the arc quenching ability of the breakers is compromised. The warning alarm alerts the user when this happens.
Working Principle of SF6 Circuit Breaker
The contacts of the breaker are closed under normal operating conditions. However, when a fault occurs in the system, the contacts are pulled apart, and an arc is formed between them. This displacement of the moving contacts is synchronized with a valve, which allows high-pressure SF6 gas to enter the arc-interrupting chamber at a pressure of around 16kg/cm^2.
SF6 gas absorbs free electrons in an arc and forms ions that don’t act as charge carriers, increasing the dielectric strength and extinguishing the arc. The gas pressure reduces up to 3kg/cm2, and it’s stored in a low-pressure reservoir, then pulled back for reuse.
Puffer piston pressure generates arc quenching pressure by attaching pistons to the moving contacts during opening operations.
Advantage
SF6 circuit breakers offer several advantages over conventional breakers.
- SF6 gas possesses excellent insulating and arc extinguishing properties, making it the ideal choice for SF6 circuit breakers.
- The gas is stable and non-flammable, and its decomposition products are non-explosive, making it safe from fire and explosion.
- The electric distance between conductors is decreased significantly due to the high dielectric strength of SF6.
- The performance of this device remains unaffected by any changes in atmospheric conditions.
- It operates without noise and avoids overvoltage since the arc extinguishes at natural current zero.
- No carbon particles are formed during arcing, meaning there is no reduction in dielectric strength.
- It requires minimal maintenance and does not need a costly compressed air system.
- SF6 is used for various purposes, such as clearing short-line faults and switching and opening unloaded transmission lines and transformer reactors without any issues.
Disadvantages
- SF6 gas can be suffocating if it leaks from the breaker tank. Because SF6 gas is heavier than air, it escapes and settles in the surrounding area, causing suffocation for operating personnel.
- The ingress of moisture into the SF6 breaker tank is extremely detrimental to the breaker, leading to multiple failures.
- As a part of regular maintenance, it is crucial to clean the internal components in a clean and dry environment.
- The transportation and maintenance of gas require a particular facility to ensure its quality.
Maintenance of SF6 Circuit Breaker
- Make sure to check for gas leaks regularly to ensure safety.
- Check mechanical components thoroughly
- Apply lubrication to the moving parts.
- Test the control circuits.
- Replace the worn-out components.
Applications
SF6 circuit breakers find various applications in the electrical industry. Some of the typical applications include the following.
- Power Transmission and Distribution: SF6 circuit breakers are commonly used in high-voltage power systems to protect transformers, circuit lines, and other crucial equipment.
- Industrial Plants: Industrial facilities use these protection devices to safeguard electrical equipment from short circuits and overloads.
- Railways: SF6 circuit breakers are utilized in railway electrification systems to guarantee uninterrupted power supply and secure power distribution.
- Substations: SF6 circuit breakers are used in power substations to regulate and safeguard the electrical grid.
- Power Generation: SF6 circuit breakers are suitable for protecting generators in power generation facilities.
- Renewable Energy: Renewable energy systems such as wind farms and solar power plants utilize them.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Sulphur Hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breakers are crucial to modern electrical systems, ensuring reliable operation and safety. Their exceptional insulating properties and high arc-quenching capability make them indispensable in high-voltage applications.