In high-voltage power distribution systems, safe and reliable switching equipment is essential. One of the most commonly used devices is the GO/GOAB Switch (Gang operated/ Gang operated Air Break Switch) . These switches are widely installed in substations and industrial power networks to isolate or connect the 11 kV and 33 kV lines.
This guide explains the GO/GOAB Switch full form, construction, working principle, parameters, and types in a simple and easy-to-read format.
Full Form of GO/GOAB Switch
- GO Switch full form: Gang Operated Switch
- GOAB Switch full form: Gang Operated Air Break Switch
- AB Switch full form: Air Break Switch
- GOS full form in electrical: Gang Operated Switch
A GOS –gang operated switch-means that all three phases of a high-voltage line are operated simultaneously (in a group or “gang”) using a single handle or operating mechanism.
What is a GO Switch?
A Gang Operated (GO) Switch is an outdoor high-voltage switch used in 11 kV and 33 kV systems to connect or disconnect the power supply. It is one of the most economical, reliable, and widely used devices in HT distribution networks.
Key Functions:
- Isolate feeders or transformers for maintenance.
- Provide manual switching control of HT lines.
- Act as an isolation point during fault conditions.
- Ensure safe working for linemen and engineers.
Note: The GO Switch is not designed to break heavy load currents directly. It should always be operated after disconnecting the load (either by circuit breakers or drop-out fuses).
Construction of GO/GOAB Switch
The design of a GOAB switch is simple but robust, ensuring it can withstand harsh outdoor conditions, mechanical stress, and electrical faults.
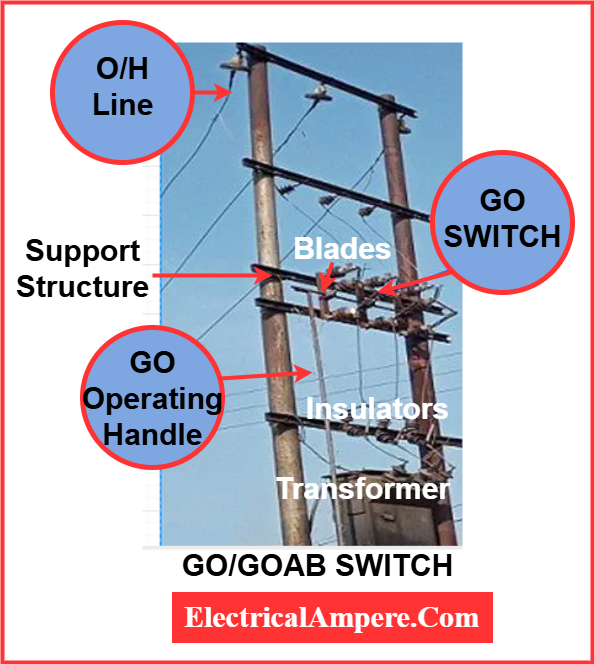
Major Components:
- Support Structure (Poles):
- Usually made of iron or concrete.
- Provides mechanical strength for mounting the switch assembly.
- Insulators (Post Type):
- Made of porcelain or polymer composite.
- Hold the live parts and provide insulation from the earthed support.
- Switch Blades/Arms:
- Conducting metal parts that open or close the circuit.
- Mounted horizontally or vertically depending on the design.
- Phase Coupling Shaft:
- A connecting shaft that links all three phases together.
- Ensures simultaneous (gang) operation.
- Operating Rod and Handle:
- The handle is mounted on the pole (around 4 ft above ground).
- Transmits manual force to operate the switch blades.
- Arcing Horns:
- Specially designed metal horns fitted on contacts.
- Control and extinguish the arc safely during opening.
This rugged construction allows GOAB switches to function reliably for years with minimal maintenance.
Working Principle of GO Switch
The working principle of a GOAB switch is based on the air-break mechanism.
- When the switch is opened manually, air acts as the dielectric medium.
- The switch has arcing horns on the blades and contacts.
- As the blades separate, the arc forms, stretches, and finally extinguishes in the air.
- Since air is an excellent medium for arc quenching, the switch operates safely and reliably.
Important Note: GO switches (Gang Operated Switches) are not designed to interrupt the circuit at load current. They should always be operated after disconnecting the load.
Parameters of GO Switch (11 kV & 33 kV)
| Parameter | 11 kV GO Switch | 33 kV GO Switch |
| System Voltage | 11 kV | 33 kV |
| Highest System Voltage | 12 kV | 36 kV |
| Temperature Range | 40°C – 60°C | 40°C – 60°C |
| Relative Humidity | 70% – 100% | 70% – 100% |
| Rated Normal Current | 400 A | 400 A |
| Short Circuit Current (3 sec) | 31.5 kA | 25 kA |
| Highest Load Capacity | 400 A | 400 A |
These parameters define the voltage rating, current carrying capacity, and fault tolerance of the switch.
Types of GO Switch
Based on installation, application, and mechanical arrangement, the following types of GOAB switches are used:
- Horizontal Mounting Type – Blades mounted horizontally.
- Vertical Mounting Type – Blades mounted vertically, widely used in distribution.
- Rotating Type – Switch blades rotate around an axis.
- Composite Polymer AB Switch – Uses polymer insulators for improved strength and lighter weight.
- Double Stack Tilting Type – Designed for compact substations.
- GO-DO Combined Switch – Combination of Gang Operated switch and Drop-Out fuse for added protection.
- Single Phase GOAB Switch – Used where only one phase needs isolation.
Choice of type depends on network design, available space, and operational needs.
Health Testing of GO Switch
To ensure reliable performance and long service life, GO and GOAB switches undergo a series of tests. Each test verifies specific electrical or mechanical properties of the switch under operating conditions.
Common Tests:
- Temperature Rise Test – Ensures contacts don’t overheat.
- On-Load Breaking Capacity Test – Checks load current handling.
- Short-Time Current Test – Verifies ability to withstand fault current.
- Off-Load Breaking Capacity Test – Ensures safe isolation without load.
- Line Charging Breaking Test – For switching long transmission lines.
- Dielectric Strength Test – Ensures insulation performance.
- Mechanical Endurance Test – Checks durability of operating mechanism.
Advantages of GOAB Switch
- Simple design and low cost.
- Easy to operate and maintain.
- Provides reliable isolation for HT systems.
- Long life with minimal maintenance.
- Can withstand outdoor environmental stress.
Conclusion
The GO/GOAB Switch (Gang Operated Air Break Switch) is a vital component of 11 kV and 33 kV power distribution networks. With its rugged construction, air-break operation, and simultaneous (ganged) switching, it ensures safe and efficient isolation of feeders and transformers.
From horizontal and vertical mounting types to GO-DO combined switches, these devices are versatile and reliable. Regular testing ensures long life and dependable performance.
In summary, the GO/GOAB Switch is a cost-effective, field-proven, and essential switchgear for HT power systems.
Related Articles: