The double earthing ensures the safety of electrical equipment and persons working on it. The frame or enclosure is connected to two separate earth pits; similarly, the neutral point is also connected to two separate earth pits.
This double earthing meaning helps in understanding what is double earthing and why it is important for safety.
In practice, the installation must follow the proper double earthing standard as per regulations to ensure maximum protection.
Types of Earthing: Equipment and System Earthing
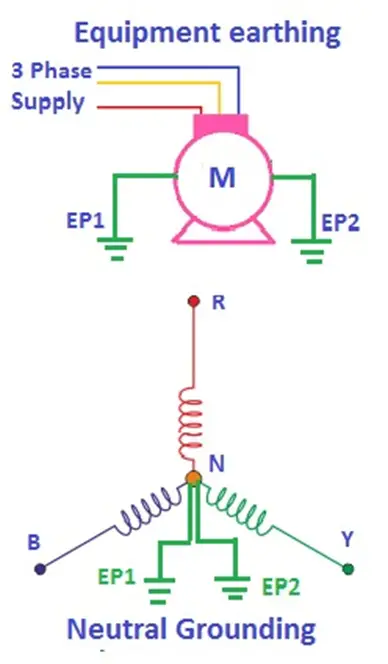
There are two types of earthing used in electrical systems: equipment earthing (or body earthing) and system earthing (neutral grounding). In equipment earthing, the non-current-carrying metallic part of the electrical enclosure is connected to the earth, and in system earthing or grounding neutral point is connected to the earth.
Thus, there is a need for double body earthing for the frame and system ground. The system earthing is also called system grounding.
Why Earthing is Necessary?
The conducting part, which remains at zero potential in normal conditions, attains phase voltage when the insulation of the electrical panel fails. In this condition, the panel body attains phase voltage. If earthing is not done and anybody touches the frame at the time of fault, one may get an electric shock. This explains why earthing is required and why is earthing done.
The purpose of earthing is to divert the current to earth so as to maintain the metallic frame potential to zero. The earth has very low resistance, and fault current starts flowing towards the ground. The protection circuit senses the earth’s fault current and trips the supply system.
Thus, the earthing provides protection against an electric shock fire and machine protection.
The earthing resistance value must be as minimal as possible. The earthing pit resistance must be minimal, and the earthing strip or conducting wire used between the equipment frame and the earth pit should have very low resistance. Double earthing or 2-points earthing causes the equivalent resistance to lower, thus ensuring enhanced protection.
In a similar way, the neutral point of the supply system is at zero potential under normal operating conditions. However, neutral point voltages rise in faulty conditions and the other healthy phase voltage also rises if the system is ungrounded. This condition may lead to insulation failure due to high voltage. Therefore, in order to maintain the system stability, the neutral point is earthed. This is called the grounding or system grounding.
Why Double Earthing is Necessary?
We are connecting the frame of the electrical appliance to the earth and also connecting the neutral point to the earth, so why is double earthing recommended? Why not? Single-point earthing is OK.
Two separate earthing circuit is made and connected to the frame of the equipment and the neutral of the supply system. Thus total of four numbers of earth pit are required: two numbers for frame earthing and two for neutral earthing. Double earthing is required for safety of the equipment and personnel.
A double earthing diagram can help visualize the setup, as shown in the figure below. The motor frame is connected to two separate body earthing points, ensuring both personnel safety and reliable fault current flow.
Difference Between Single Earthing and Double Earthing
Understanding the difference between single and dual earthing helps in selecting the right method for equipment and systems. While single earthing provides basic protection, dual earthing offer enhanced safety and reliability.
The table below summarizes the key differences:
| Aspect | Single Earthing | Dual Earthing |
| Definition | One earth connection for the equipment or system | Two separate earth connections: one for equipment frame, one for system neutral |
| Number of Earth Pits | 1 | 2 (for frame) + 2 (for neutral) |
| Safety | Basic protection | Enhanced safety for personnel and equipment |
| Reliability | Less reliable if earth path fails | More reliable; fault current always has a path |
| Resistance | Higher effective resistance | Lower effective resistance due to parallel paths |
| Common Use | Simple equipment, less critical systems | Motors, welding machines, and critical panels |
Advantages of Double Earthing
The double earthing provides the following advantages.
- If there is one earth circuit, the fault current flows through the circuit. However, if the earth circuit is not closed, the frame or enclosure body may attain live potential. However, if two circuits are there, one circuit will divert the current to Earth if one of the circuits gets defective. Thus, the earthing system reliability gets enhanced with double earthing.
- In the event of a fault, the current will flow in two earth circuits for a double earthing scheme. The effective resistance of the circuit is always less than the resistance of one circuit because both circuits are in parallel. If we connect 2 ohms resistance in parallel, the equivalent resistance is 1 Ohm. The same property applies here. The low resistance of the earth circuit causes easy flow of earth fault current to earth. For example, in double earthing for welding machine or motor double earthing, fault currents can safely travel to the ground.
Conclusion: Importance of Proper Double Earthing
Double earthing ensures maximum safety for both personnel and electrical equipment. Proper design and low-resistance connections enhance reliability and reduce the risk of electric shock or equipment damage.
Related Articles: