Understanding materials used in electrical and electronic systems is crucial, especially when it comes to dielectrics and insulators. While these terms are often used interchangeably, there are important differences between them. In this article, we’ll explore the difference between dielectric and insulator, examples, their properties, and applications.
What is an Insulator?
An insulator is a material that resists the flow of electric current. It is widely used in electrical systems to prevent unwanted current leakage and protect users and devices from electric shocks.

Key characteristics of insulators:
- High resistance to electrical current
- Low conductivity
- Used to cover wires, cables, and other electrical components
Common examples of insulators:
- Rubber
- Plastic
- Glass
- Ceramic
Insulators are generally used for safety and structural purposes in electrical circuits.
What is a Dielectric?
A dielectric is a special type of insulating material that can be polarized when an electric field is applied. Dielectrics do not conduct electricity, but they can store electrical energy in the form of an electric field. This property makes them essential in capacitors and other energy storage devices.
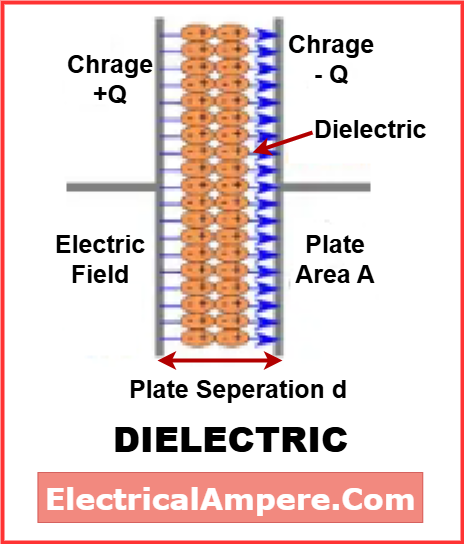
Key characteristics of dielectrics:
- Can be polarized in an electric field
- Store electrical energy
- High dielectric constant (ability to store charge)
Examples of dielectric materials:
- Mica
- Teflon
- Glass
- Ceramic
Notice that while all dielectrics are insulators, not all insulators can act as effective dielectrics.
Key Differences Between Dielectric and Insulator
| Feature | Insulator | Dielectric |
| Definition | Material that resists electric current | Insulating material that can be polarized and store electrical energy |
| Function | Prevents current flow | Stores electrical energy in an electric field |
| Electric Field | Does not interact significantly with the electric field | Can be polarized under electric field |
| Examples | Rubber, Plastic, Glass | Mica, Teflon, Ceramic |
| Dielectric Constant | Not a primary consideration | High dielectric constant is important |
| Application | Cable covering, electrical insulation | Capacitors, energy storage, high-frequency circuits |
Additional Comparisons
- Difference between dielectric and conductor: Conductors allow current flow freely, whereas dielectrics resist current but can store energy.
- Dielectric constant for insulator: The dielectric constant is a measure of how well a material can store electrical energy. While insulators generally have low dielectric constants, dielectrics are chosen for their high dielectric constants to improve efficiency in devices like capacitors.
Dielectric Examples in Daily Life
- Mica: Used in capacitors and electronic equipment due to its high stability
- Glass: Found in high-voltage insulators and circuit boards
- Teflon: Used in cables and electronic components
- Ceramic: Common in capacitors and insulating layers
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between dielectric and insulator is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems. Insulators primarily prevent current leakage, whereas dielectrics not only insulate but also store electrical energy. Choosing the right material depends on the specific application, whether for safety, efficiency, or energy storage.
By knowing these distinctions, engineers and hobbyists can make better decisions for both electrical insulation and energy storage applications.
Related Articles: