Centrifugal Switch: Learn its definition, working principle, symbol, testing methods, and role in induction motors. Understand its importance in motor startup and operation.
What Is a Centrifugal Switch?
A centrifugal switch is an electrical component that operates based on the centrifugal force generated by a rotating motor shaft. It is primarily used in single-phase induction motors to control the start-up process by disconnecting the starting winding once the motor reaches a predefined speed. This mechanism ensures efficient motor operation and prevents damage to the winding due to excessive current flow.
How Does a Centrifugal Switch Work?
A centrifugal switch is commonly found in single-phase induction motors, particularly in split-phase and capacitor-start motors. These motors require an additional winding during startup, which must be disconnected once the motor attains sufficient speed. The centrifugal switch performs this function automatically based on the motor’s rotational speed.
Working Principle:
- Initial State (Motor Off): When the motor is at rest, the centrifugal switch remains closed, allowing current to flow through the starting winding.
- Starting Phase: Upon powering the motor, the starting winding receives current, generating extra torque to initiate rotation.
- Operational Phase: As the motor gains speed (typically 70-80% of full speed), centrifugal force causes the switch’s mechanism to open, disconnecting the starting winding.
- Steady-State Operation: The motor continues to run on the main winding, while the starting winding remains inactive.
- Motor Shut-off: When the motor is turned off, the centrifugal switch resets to its original closed position, ready for the next start-up cycle.
The centrifugal switch plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of motors by preventing continuous current flow through the starting winding, which could otherwise lead to overheating and winding failure.
Centrifugal Switch Symbol
The centrifugal switch is represented by a specific symbol in electrical schematics. This symbol visually conveys its role in circuit control and connectivity. A centrifugal switch symbol typically includes a movable contact that is responsive to centrifugal force, demonstrating its automatic disengagement at high speeds.

A switch is an essential electrical component that controls the flow of current in a circuit by connecting or disconnecting the conductive path, altering, or redirecting the electrical flow.
A centrifugal switch operates based on shaft rotation, responding to speed or direction changes by opening only as the speed increases.
It is represented as a switch that functions based on the rotation of the shaft. When the motor reaches a predetermined speed, the switch automatically opens. In motor wiring diagrams, it is commonly marked to indicate its specific role in the circuit.
Centrifugal Switch in Induction Motors
To understand the role of a centrifugal switch in induction motors, it’s essential to first grasp their basic structure. Induction motors consist of a stator with a primary winding and an auxiliary winding. When a single-phase AC current is applied, the stator winding alone cannot generate the necessary rotating magnetic field to produce starting torque. To overcome this, an auxiliary winding is included.
The auxiliary winding creates a secondary magnetic field that is out of phase with the main stator field, producing the required starting torque to initiate motor rotation. Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the rotor generates a self-sustaining magnetic field, eliminating the need for the auxiliary winding.
At this point, the centrifugal switch comes into play. It automatically disconnects the auxiliary winding from the circuit when the motor reaches a predetermined percentage of its synchronous speed, ensuring efficient operation and preventing overheating.
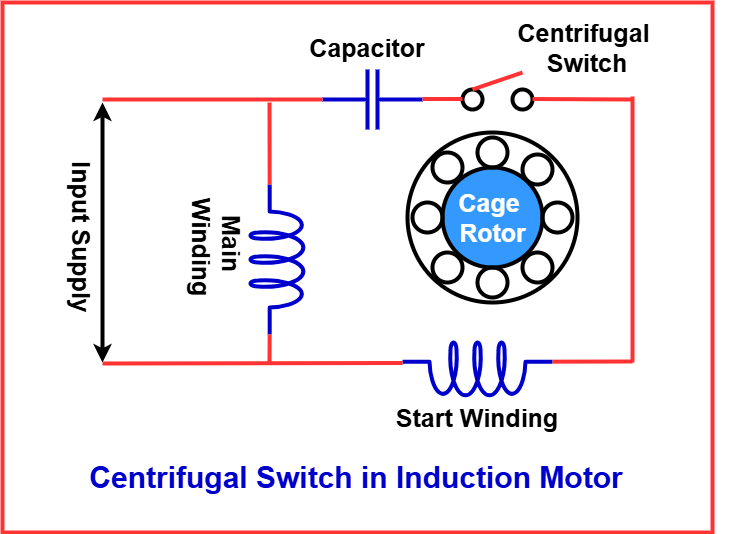
How to Test a Centrifugal Switch?
Testing a centrifugal switch ensures its proper functionality and prevents motor failures. Here are the key steps to test the switch:
Testing Procedure:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the switch for physical wear, dirt accumulation, or loose connections.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the switch when the motor is at rest and in motion.
- When stationary, the switch should show continuity (closed state).
- When running at full speed, the switch should show an open circuit.
- Motor Operation Test: Start the motor and observe whether the switch disengages at the right speed.
- Resistance Measurement: Measure the resistance across the switch contacts to ensure minimal resistance when closed.
- Mechanical Functionality: Verify that the centrifugal mechanism moves freely and engages/disengages without obstruction.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting:
- Switch Does Not Open: If the switch fails to open, the starting winding remains active, leading to overheating and possible motor burnout.
- Switch Remains Open: If the switch does not close upon shutdown, the motor may struggle to restart.
- Dirty or Worn Contacts: Clean or replace the switch contacts if dirt or oxidation is causing poor connectivity.
Impact of a Faulty Centrifugal Switch
A malfunctioning switch can lead to serious motor issues, including:
- Overheating of Starting Winding: If the switch does not open, continuous current flow can burn out the winding.
- Reduced Motor Efficiency: A faulty switch can cause excessive energy consumption.
- Motor Failure: Prolonged operation with a defective switch can lead to permanent motor damage.
Why Are Centrifugal Switches Used in Single-Phase Motors?
Single-phase induction motors inherently lack self-starting capability due to the absence of a rotating magnetic field. To overcome this limitation, a starting winding provides an initial torque boost. The centrifugal switch ensures that this additional winding is disconnected once the motor reaches operational speed, enhancing efficiency and longevity.
Effect of a Centrifugal Switch Not Disconnecting After Motor Startup
The centrifugal switch must disconnect when the motor reaches approximately 70–80% of its full speed. If it remains engaged, excessive current will continue flowing through the starting winding, leading to overheating and eventual failure of both the winding and the motor. Additionally, the motor may not achieve its optimal speed and current levels.
Do All Single-Phase Motors Have a Centrifugal Switch?
Not all single-phase motors use a centrifugal switch. In some designs, the start winding remains active as an auxiliary winding when the motor reaches running speed, effectively functioning as a two-phase motor. These motors are considered highly reliable since they eliminate the need for a switch.
Which Type of Split-Phase Motor Does Not Typically Have a Centrifugal Switch?
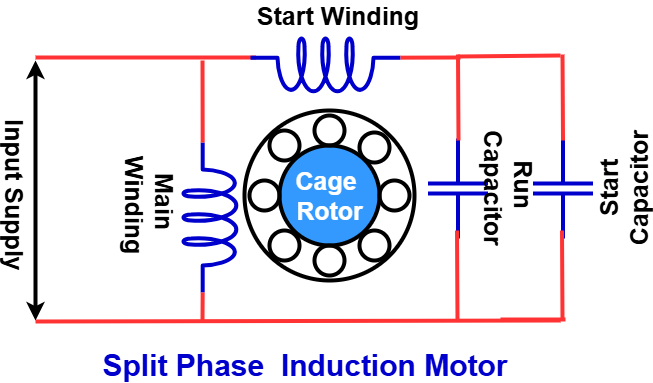
The Capacitor-Start Capacitor-Run Motor generally does not include a centrifugal switch to disconnect the starting winding.
This motor consists of a cage rotor and a stator with two windings: main winding and auxiliary winding, positioned 90 degrees apart. It uses two capacitors:
- A starting capacitor, which assists during startup.
- A run capacitor, which remains connected for continuous operation.
Because both capacitors are integral to the motor’s function, this motor is often called a Two-Value Capacitor Motor or a Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Motor.
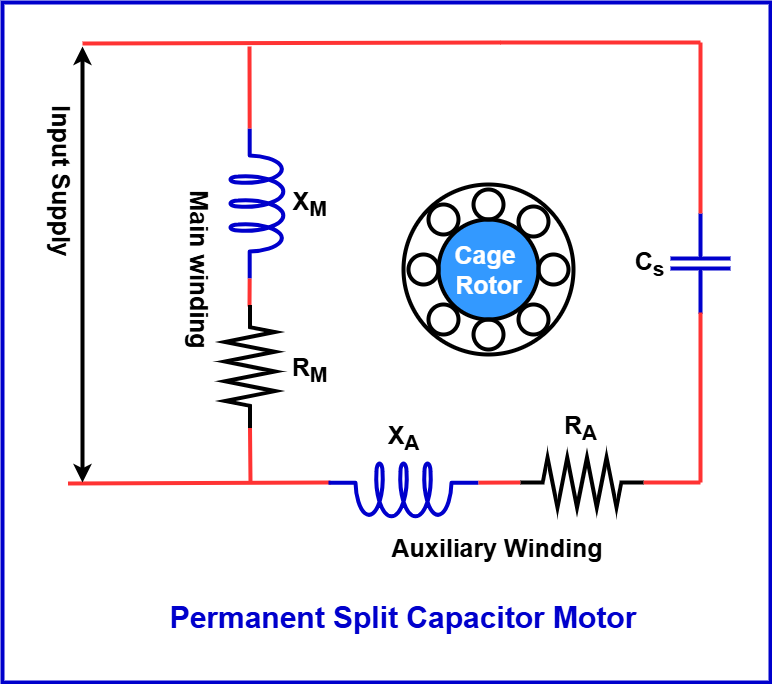
Similarly, the Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) Motor, another type of split-phase induction motor, does not require a centrifugal switch. It has a single permanently connected capacitor in series with the starting winding. Unlike other motors that disconnect the capacitor after startup, the PSC motor keeps it in the circuit at all times, eliminating the need for a starting switch. This is why it is also called a Single-Value Capacitor Motor.
Applications of Centrifugal Switches:
- Household Appliances: Used in washing machines, fans, and air conditioners.
- Industrial Equipment: Common in compressors, pumps, and grinders.
- Automotive Systems: Found in certain engine starter circuits.
Conclusion
The centrifugal switch is a critical component in single-phase induction motors, ensuring smooth startup and efficient operation. By automatically disconnecting the starting winding, it prevents overheating and enhances motor durability. Regular testing and maintenance of the switch are essential to avoid motor failures and ensure reliable performance. Understanding its working principle, symbol representation, and testing methods can help in troubleshooting and maintaining motor efficiency.
Read Next: