Learn all about AT & C losses — their meaning, formula, main causes, and best practices to reduce them effectively. Understand how technical and commercial losses impact power distribution and what steps can help minimize at and c losses for improved efficiency.
In the power industry, the journey of electricity—from generation to transmission to final distribution—involves inevitable energy losses at every stage. But among these, distribution losses account for the highest share, primarily due to unplanned infrastructure, aging equipment, theft, and inefficient billing systems. These losses are collectively known as AT & C losses.
India, for instance, records an average of 35% AT&C losses, a figure that varies widely across states—from as low as 9.13% in Pondicherry to as high as 85.49% in Manipur (PFC Report 2012-13). Reducing these losses is crucial to improving financial health of utilities and ensuring quality power to consumers.
What are AT & C Losses?
AT & C losses stand for Aggregate Technical and Commercial losses. It is a comprehensive metric that represents both technical losses (due to energy dissipation in electrical components) and commercial losses (arising from theft, defective meters, and poor billing systems).
In simple terms:
🔹 Technical losses: Occur due to equipment inefficiencies like line losses, transformer losses, etc.
🔹 Commercial losses: Arise from electricity theft, faulty metering, billing inefficiencies, and poor collection practices.
AT & C Losses Formula
The AT&C losses formula is as follows:
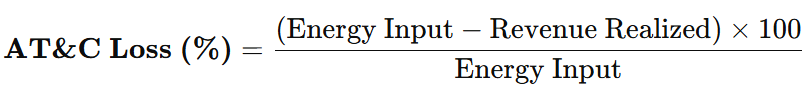
Where:
- Energy Input is the total energy supplied at the distribution point.
- Revenue Realized is the portion of billed energy that is actually collected.
Example: If the total energy input to the distribution system is 1,000,000 kWh, and the energy billed to consumers is 650,000 kWh, then:
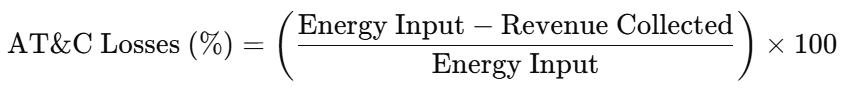
so,
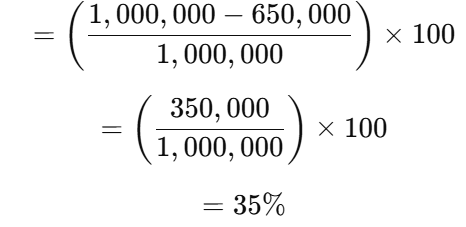
Alternatively, another widely used formula for estimation is:
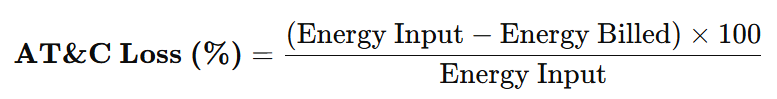
This formula accounts for both technical and commercial components and shows how much of the input energy is actually accounted for and paid.
Why Are AT&C Losses So High in India?
Several factors contribute to high AT&C losses in India:
- Aging and unplanned distribution networks
- Electricity theft and unauthorized connections
- Inefficient metering systems
- Low metering and billing coverage
- Manual billing errors and delayed collections
- Lack of automation and smart infrastructure
How to Reduce AT & C Losses: Technical Solutions
Technical losses arise primarily from inefficiencies in equipment such as transformers, power lines, and inadequate maintenance of plant and machinery. These losses can be significantly reduced by addressing these issues. The following measures can help minimize technical losses:
1. Network Reconfiguration
Re-structuring distribution networks helps improve load balancing and reliability. It provides a solution to manage rising power demand while enhancing system reliability. This includes constructing additional high voltage distribution lines wherever technically and economically viable.
2. Reduction in LT Lines
Reducing low-tension lines minimizes current flow and line losses, especially when HT (High Tension) distribution systems are adopted.
3. Power Factor Improvement
Installing Automatic Power Factor Controllers (APFCs) helps bring power factor close to unity, thus reducing energy wastage.
4. Voltage Regulation
Using automatic voltage boosters ensures optimal voltage levels and avoids overloading, thereby enhancing power quality, protecting sensitive equipment, improving energy efficiency, and maintaining system reliability during peak and fluctuating demand conditions.
5. Load Balancing
Proper three-phase load balancing reduces losses and improves overall system stability by minimizing neutral current, enhancing equipment efficiency, and ensuring consistent voltage regulation across the network.
6. Better Transformers
Use of amorphous core transformers reduces iron and copper losses.
7. Periodic Audits and Load Research
Energy audits and load analysis reveal inefficiencies and help in planning corrective measures.
8. Preventive Maintenance
Routine maintenance reduces outages and technical breakdowns.
Reducing Commercial Losses: Administrative & Technological Measures
In developed countries, commercial losses are minimal; however, the scenario is quite different in many developing nations. One of the primary contributors to high commercial losses is electricity theft. This theft can occur through various means, such as illegal tapping of power lines, tampering with meters, or bypassing them entirely. To effectively reduce these losses, several key strategies must be implemented.
1. Smart Metering
Smart meters are advanced digital devices designed to enhance energy management and reduce losses in the power distribution system. They come equipped with several key features:
a. They can record real-time or near real-time electricity consumption, as well as energy export data.
b. They allow for meter reading both locally and remotely.
c. They support remote connection and disconnection of electricity supply.
d. They enable remote communication via Power Line Carrier (PLC) or wireless modems such as GSM.
These devices are also known as Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) or part of the broader Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI).
According to various reports, electricity theft in many developing countries accounts for 20% to 35% of distribution losses. To curb these losses, several technologies and methods have been proposed, including:
- Automatic meter reading systems integrated with GSM communication.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems that analyze consumption patterns for anomaly detection.
- Power line impedance techniques to detect unauthorized tapping.
- Injection of unwanted harmonics to disrupt power supply to illegal users.
In conclusion, replacing outdated meters with smart meters is a crucial step toward reducing AT&C losses, as they enable real-time consumption tracking, remote meter reading and disconnection, as well as effective theft detection and loss monitoring.
2. Intelligent Control Systems and Harmonic Distortion
Advanced control systems, when integrated into the electric grid, not only improve power quality but also help deter electricity theft. Intelligent control systems should be tailored to specific network conditions for optimal results. When properly implemented, these technologies significantly enhance the reliability, efficiency, and security of the power distribution network.
3. Law Enforcement
Strict laws and immediate action against electricity theft are necessary. This includes disconnecting supply and imposing penalties.
4. Automation
Substation automation and distribution automation play a vital role in identifying losses and enabling timely corrective actions, thereby enhancing system efficiency and reducing both technical and commercial losses. Implement SCADA systems for real-time load management and fault detection.
5. IT Integration
Improve billing systems with:
- Spot billing
- Mobile meter reading
- Online payments
- Complaint redressal systems
6. Customer-Centric Approaches
Set up call centers, deploy MIS, and create transparent billing platforms to improve consumer trust and reduce intentional non-payment.
Best Practices in Reducing AT&C Losses
- High Voltage Distribution System (HVDS): Reduces theft by limiting accessibility.
- Aerial Bundled (AB) Cables: Make tapping into lines difficult.
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): Enables proactive billing, monitoring, and disconnection.
Innovative Technologies for AT&C Losses Reduction
Emerging technologies are playing a vital role in tackling AT&C losses:
- Artificial Intelligence for consumption pattern analysis and theft detection.
- Power Line Communication for real-time data transfer.
- Custom Power Devices for voltage regulation, harmonic filtering, and reactive power management.
Government Schemes for AT&C Losses Reduction
1. R-APDRP
Revised Accelerated Power Development and Reforms Programme to strengthen urban infrastructure.
2. DDUGJY
Deen Dayal Upadhyay Gram Jyoti Yojana targets rural distribution improvement. This Scheme aims to strengthen and upgrade the sub-transmission and distribution infrastructure in rural areas. The scheme is designed to ensure reliable, high-quality power supply while significantly reducing distribution losses.
3. IPDS
Integrated Power Development Scheme focuses on urban areas with high losses and inadequate infrastructure.
Conclusion
AT & C losses remain a significant challenge for the Indian power sector, draining both revenue and energy. With proper planning, adoption of smart technologies, improved governance, and consumer participation, these losses can be drastically reduced. It’s not just about preventing theft or upgrading lines—it’s about creating a smarter, more efficient, and transparent energy system.
Reducing AT&C losses not only ensures financial sustainability of power utilities but also improves the reliability and quality of power for consumers. By working together—governments, utilities, technologists, and citizens—we can transform the power sector for the better.
Loss reduction in the distribution sector can be effectively achieved through the implementation of advanced technological solutions, government initiatives, and strict enforcement of laws. Imposing stringent penalties for electricity theft, including immediate disconnection and prolonged restriction on reconnection, can deter illegal activities.
The integration of intelligent control systems enhances power quality and helps prevent unauthorized usage. Alongside adequate funding from various schemes, strong commitment, ownership of the distribution network, and active stakeholder participation are crucial. These combined efforts can lead India towards a theft-free distribution system, potentially saving around 35% of losses annually, which is approximately Rs. 40,000 crore.
Read Next: