Knowing how much electricity your home appliances consume is key to managing your energy bills, saving money, and making your household more energy-efficient. In this guide, we’ll explore power consumption for home appliances, show examples in kWh, and give practical tips to reduce electricity usage.
What is Power Consumption in kWh?
Power consumption measures how much electricity an appliance uses over time. It’s usually expressed in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- 1 kWh = Using 1 kilowatt (1,000 watts) of power for 1 hour.
- Example: A 100 W bulb running for 10 hours consumes:
100 W×10 hours=1000 Wh=1 kWh=1 Unit ( unit of electricity)
Electricity bills are based on kWh consumed, making it important to know the energy usage of your household appliances.
Read detiled article: How to Calculate Electricity Bill from kWh (Units)
Factors Affecting Power Consumption
- Power Rating of Appliance (Wattage): Higher wattage appliances consume more electricity.
- Daily Usage Duration: The longer an appliance runs, the more energy it uses.
- Appliance Efficiency: Modern energy-efficient appliances consume less power than older models.
- Operating Conditions: For example, air conditioners consume more power in hot climates.
Average Power Consumption of Home Appliances
Here’s a comprehensive table of common household appliances with approximate power consumption:
| Appliance | Power (W) | Average Daily Use (hrs) | Energy Consumed (kWh/day) |
| LED Bulb (10 W) | 10 | 5 | 0.05 |
| CFL Bulb (15 W) | 15 | 5 | 0.075 |
| Tube Light (40 W) | 40 | 6 | 0.24 |
| Refrigerator (150 W) | 150 | 24 | 3.6 |
| Washing Machine (500 W) | 500 | 1 | 0.5 |
| Microwave Oven (1,000 W) | 1,000 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Air Conditioner 1.5 Ton | 1,500 | 8 | 12 |
| Water Heater (1,500 W) | 1,500 | 1 | 1.5 |
| Electric Iron (1,000 W) | 1,000 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Laptop (65 W) | 65 | 8 | 0.52 |
| Desktop Computer (200 W) | 200 | 8 | 1.6 |
| TV LED 40-inch (100 W) | 100 | 5 | 0.5 |
| Ceiling Fan (75 W) | 75 | 8 | 0.6 |
| Water Pump (750 W) | 750 | 2 | 1.5 |
| Electric Kettle (2,000 W) | 2,000 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| Oven (2,000 W) | 2,000 | 1 | 2 |
| Hair Dryer (1,500 W) | 1,500 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Electric Geyser (2,000 W) | 2,000 | 1 | 2 |
| Coffee Maker (1,000 W) | 1,000 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Vacuum Cleaner (1,200 W) | 1,200 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Microwave Convection (1,200 W) | 1,200 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Rice Cooker (700 W) | 700 | 1 | 0.7 |
| Electric Oven Toaster (800 W) | 800 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| Induction Cooktop (1,500 W) | 1,500 | 1 | 1.5 |
| Water Dispenser (100 W) | 100 | 24 | 2.4 |
| Air Purifier (50 W) | 50 | 10 | 0.5 |
| Electric Grill (1,200 W) | 1,200 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Deep Freezer (200 W) | 200 | 24 | 4.8 |
| Blender (500 W) | 500 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Toaster (800 W) | 800 | 0.2 | 0.16 |
This table helps you estimate energy consumption by household appliances, identify high-consumption devices, and take action to reduce electricity bills.
How to Calculate Electricity Consumption
You can calculate energy consumption for any appliance using:
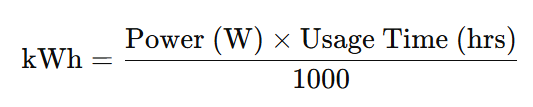
Example 1: A 1,500 W air conditioner runs for 8 hours:
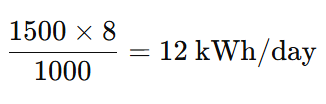
Example 2: A 65 W laptop runs for 8 hours:
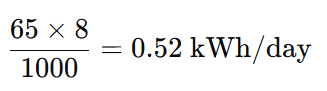
This simple formula can help you calculate appliances’ power consumption in kWh for your home.
Tips to Reduce Electricity Consumption at Home
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Choose Energy Star-rated or inverter models.
- Unplug appliances when not in use: Many devices draw power even in standby mode.
- Time your usage: Avoid running high-power appliances simultaneously.
- Regular maintenance: Clean filters in ACs and refrigerators for efficient operation.
- Use smart plugs and meters: Track electricity consumption for each appliance.
- Replace old lighting: Switch to LED bulbs and tubes, which use less power.
Benefits of Tracking Household Appliance Energy Consumption
- Lower electricity bills: Identify which devices consume the most power.
- Energy conservation: Reduce wastage and carbon footprint.
- Better appliance management: Know when to replace or repair appliances.
Conclusion
Understanding home appliances electricity consumption helps manage costs, improve energy efficiency, and make environmentally conscious decisions. By monitoring power consumption appliances, switching to energy-efficient models, and practicing mindful usage, you can reduce electricity bills while maintaining comfort at home.
Related Articles: