The lead-acid battery life is significantly impacted by the extent to which they are discharged. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the intended usage – whether it is for deep cycle, shallow cycle, or floating charge. In the event that a shallow-cycle battery is utilized for deep-cycle purposes, it will inevitably fail prematurely and not endure as long.
The life of a lead acid battery depends on the operating conditions and the effective maintenance practices followed to check battery health regularly. The useful life of the lead acid battery can be achieved up to its guaranteed life if the charging and discharging cycles of the battery are as per the ideal operating procedure.
The major reasons for battery failures or reduced battery life are loss of active material, insulation failure of the separator, and damage to the connection points of the battery due to rapid oxidation. The following reasons generally contribute to the reduction of the useful life of the battery.

Factors affecting the life of lead-acid batteries
The following factors negatively impact the life of lead-acid batteries
- Overcharging
- Undercharging
- Local Galvanic Action
- Loss of Active Material
- Excessive Rate of Charge or Discharge
- Electrolytic Action
- Entrance of Impurities
- Low Water Level
Overcharging
The battery charging equation is given below.

Lead sulfate converts into the active material at the anode and cathode during the charging process. The oxygen(O2) gas is liberated at the anode, and the hydrogen(H2) gas is liberated at the cathode when the battery is about to charge. If the battery is charged above capacity, pernicious effects will happen.
- The gas formation during overcharging causes water to break down into hydrogen and oxygen gas. The gas formed interacts with the active material, which scrubs the active material. As a result, the battery charging and discharging capacity deteriorated for the next cycles.
- Excessive charging reduces the water level of the battery. Rapidly lowering the water level in the battery indicates battery overcharging.
- The overcharging of the battery causes excessive heat inside the battery. Excessive heat can cause buckling and wrapping, which may eventually cause damage to the separators.
Undercharging
If the battery is not fully charged, it can not deliver the rated amperage to the load. The sulphation formation on the plates is likely to occur because the specific gravity of the battery is low. The discharge equation of the lead acid battery is given below.
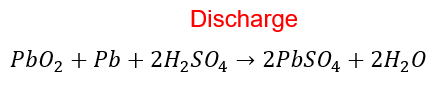
- The white material forming on the plate is called Sulphation of the plates. Sulphation can cause the bending( buckling) of the plates and the formation of metallic lead in the separator.
- A battery can not deliver the rated amperage to load if the battery is undercharged.
Local Galvanic Action
If the local galvanic action is formed in the entire battery, more charging current is required to boost the battery voltage. Excessive charging will reduce the useful life of the battery. If the local galvanic action is formed in a particular battery cell, overcharging the battery will not boost the battery voltage. The only solution in this case is charging such a battery separately.
Loss of Active Material
The loss of the active material can be seen as sediment in the bottom of the battery. If the active material loss occurs, the battery will draw more current for charging, and the ampere-hour capacity of the battery gets lowered. After substantial loss of active material from the battery plates, the battery life gets lowered, and the battery must be replaced.
Excessive Rate of Charge or Discharge
The battery must be charged and discharged according to the battery’s design rating. Excessive charging and discharging cause heat inside the battery, which may damage the plates and separator.
Electrolytic Action
The electrolytic action occurs when the electrolyte comes in contact with the grid of positive plates. This can cause cracks in the grid frames, and further, it may break the plate apart.
Entrance of Impurities
The water added to the battery to maintain the specific gravity of the cell must be free from the impurities. The impurity in the distilled water may cause local galvanic action.
Low Water Level
The water level in the battery must be maintained up to the marked level on the battery. The higher acid concentration may damage the separators of battery cells and permanently damage the battery. The local galvanic action aggravates the low water level in the battery and will reduce the battery voltage.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the life of a lead acid battery is influenced by factors such as Overcharging, Undercharging, Local Galvanic Action, Loss of Active Material, Excessive Rate of Charge or Discharge, Electrolytic Action, Entrance of Impurities, and Low Water Level. You can take care of the above points to enhance the useful life of a lead acid battery.